You can use this model in the Detect Objects Using Deep Learning tool available in the Image Analyst toolbox in ArcGIS Pro. Follow the steps below to use the model for detecting well pads in images.This model can also be fine-tuned using Train Deep Learning Model tool. See Fine-tune the model page for details on how to fine-tune this model.
Supported imagery
You can use this model with multispectral Sentinel-2 (Level 2) imagery in the form of a raster product, mosaic dataset, or image service.
When using a raster product, ensure that you choose the BOA Reflectance product while adding the imagery to your map. When using a mosaic dataset, ensure that you choose the Sentinel-2 raster type and BOA Reflectance processing template while creating the mosaic. This mosaic dataset can also be published as an image service and used as an input.
Ensure that the bit depth of the input is 16 Bit Unsigned, and that the processing template is set to None. You can automate creation, configuration, and population of your mosaic datasets using Mosaic Dataset Configuration Script (MDCS).
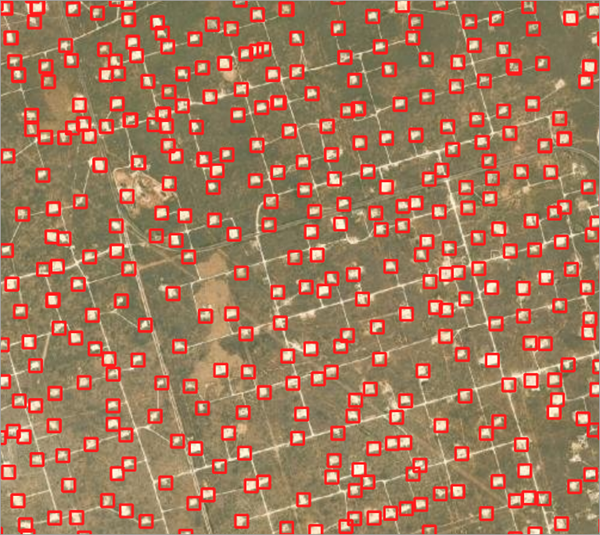
Detect well pads
Use the following steps to detect well pads from the imagery:
- Prepare data according to the following product type:
- Raster Product
- Browse to the folder housing the Sentinel-2 L2A data. Expand the folder and locate the raster product.
- Expand the Raster Product provided as an .xml file and select the BOA Reflectance derived raster dataset.

- Mosaic Dataset
- Create a Mosaic Dataset using the Create Mosaic Dataset geoprocessing tool. Set the variables on the Parameters tab as follows:
- Output Location—Select a geodatabase.
- Mosaic Dataset Name—Set the mosaic dataset name.
- Coordinate System—Select a coordinate system for the output mosaic dataset.
- Product Definition—Select None.

- To add the raster to the mosaic dataset, open the Add Rasters to Mosaic Dataset geoprocessing tool. Set the variables on the Parameters tab as follows:
- Mosaic Dataset—Select the input mosaic dataset.
- Raster Type—Select Sentinel-2 from the drop-down list.
- Processing Templates—Select BOA Reflectance from the drop-down list.
- Input Data—Select Folder from the drop-down list, browse and add the .SAFE files.

Note: You can create a multiband image through either the Composite Bands geoprocessing tool or Composite Bands raster function if required, which can be used as input for inferencing.
- Add the imagery layer in ArcGIS Pro and zoom to an area of interest.

- Browse to Tools under the Analysis tab.

- Click the Toolboxes tab in the Geoprocessing pane, select Image Analyst Tools, and browse to the Detect Objects Using Deep Learning tool under Deep Learning.

- Set the variables under the Parameters tab as follows:
- Input Raster—Select the Sentinel imagery as discussed above.
- Output Detected Objects—Set the output feature class that will contain the detected objects.
- Model Definition—Select the pretrained or fine-tuned model .dlpk file. For this use case, use the Well Pad Detection—Permian Basin model downloaded previously.
- Processing Mode— Select Process as mosaicked image mode.
- Model Arguments—Change the values of the arguments if
required.
- padding—Number of pixels at the border of image tiles from which predictions are blended for adjacent tiles. Increase its value to smooth the output while reducing edge artifacts. The maximum value of the padding can be half of the tile size value.
- threshold—The detections with a confidence score higher than this threshold are included in the result. The allowed value ranges from 0 to 1.0.
- nms_overlap—The ratio of overlap between bounding boxes with which to filter detections with lower confidence scores.
- batch_size—Number of image tiles processed in each step of the model inference. This depends on the memory of your graphic card.
- exclude_pad_detections—Specifies whether to exclude potentially truncated bounding boxes that are at the edge of each tile in the padded region. The default is True.
- radiometric_offset_correction—Corrects radiometric offset of -1000 in imageries sensed after January 25, 2022, in Sentinel 2 L2A imagery. (Note: Verify whether your data provider has already applied the offset for post January 2022 data, ; sources such as Azure and Copernicus require the radiometric_offset_correction parameter set as True. Set the parameter to False for AWS data, as it is already radiometric offset corrected and doesn't require correction again.)
- Non Maximum Suppression—Optionally, check the check box to remove the overlapping features with lower confidence.
If checked, do the following:
- Set Confidence Score Field.
- Set Class Value Field (optional).
- Set Maximum Overlap Ratio (optional).

- Set the variables under the Environments tab as follows:
- Processing Extent—Select Current Display Extent or any other option from the drop-down menu.
- Cell Size (required)—Set the value to 5.
The expected raster resolution is 5 meters.
- Processor Type—Select CPU or GPU.
It is recommended that you select GPU, if available, and set GPU ID to the GPU to be used.

- Click Run.
The output layer is added to the map.

You can zoom in to take a closer look at the results.