You can use this model in the Detect Objects Using Deep Learning tool. available in the ArcGIS Image Analyst toolbox in ArcGIS Pro. This model can also be fine-tuned using Train Deep Learning Model tool. See Fine-tune the model page for details on how to fine-tune this model.
- Download the Ship Detection (RGB) model and add the imagery layer in ArcGIS Pro.
- Add three-band satellite imagery (30 centimeter spatial resolution) and zoom
in to an area of interest.
- Click the Analysis tab and browse to Tools.
- In the Geoprocessing pane, click Toolboxes and expand Image Analyst
Tools. Select the Detect Objects Using Deep Learning tool under Deep Learning.

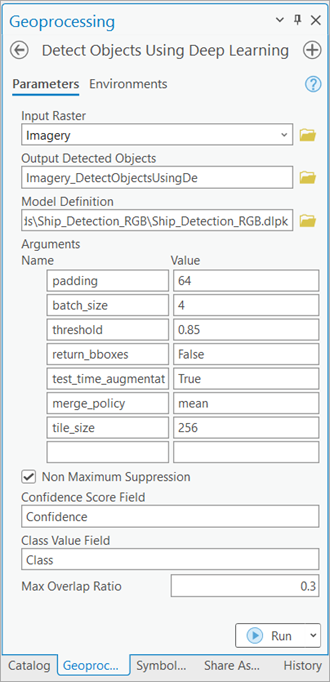
- On the Parameters tab, set the variables as follows:
- Input Raster—Select the three-band RGB imagery.
- Output Feature Class—Set the output feature layer with polygons representing the detected ships in the input imagery.
- Model Definition—Select the pretrained model .dlpk file.
- Model Arguments—Optionally, change the values of the arguments.
- padding—Number of pixels at the border of image tiles from which predictions are blended for adjacent tiles. Increase its value to smooth the output while reducing edge artifacts. The maximum value of the padding can be half of the tile size value.
- batch_size—Number of image tiles processed in each step of the model inference. This depends on the memory of your graphics card.
- threshold—The detections that have a confidence score higher than this threshold are included in the result. The allowed value ranges from 0 to 1.0.
- return_bboxes— This can be set to True to get back bounding boxes.
- tile_size—The width and height of image tiles into which the imagery is split for prediction.
- test_time_augmentation—Performs test time augmentation while predicting. This is a technique used to improve the robustness and accuracy of model predictions. It involves applying data augmentation techniques during inferencing, which means generating multiple slightly modified versions of the test data and aggregating the predictions. If true, predictions of flipped and rotated orientations of the input image will be merged into the final output and their confidence values are averaged. This may cause the confidence to fall below the threshold for objects that are only detected in a few orientations of the image.
- merge_policy—The policy for merging augmented predictions. Available options are mean, max, and min. This is only applicable when test time augmentation is used.
- Non Maximum Suppression—Optionally, check the check box to remove the overlapping features with lower confidence.
If checked, do the following:
- Set Confidence Score Field.
- Optionally, set Class Value Field.
- Optionally, set Max Overlap Ratio.
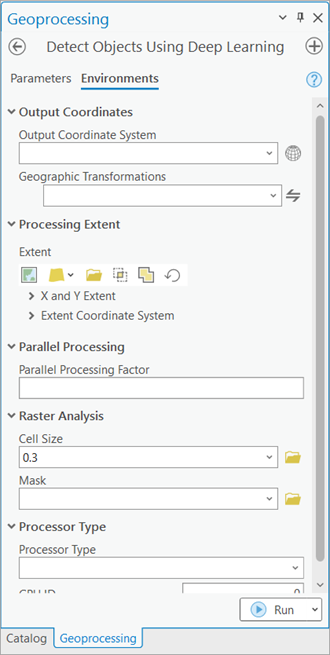
- On the Environments tab, set the variables as follows:
- Processing Extent—Select Current Display Extent or any other option from the drop-down menu.
- Cell Size—Set the value to 0.3.
The expected raster resolution is 30 centimeters.
- Processor Type—Select CPU or GPU as needed.
It is recommended that you select GPU, if available, and set GPU ID to the GPU to be used.
- Click Run.
The output layer is added to the map.
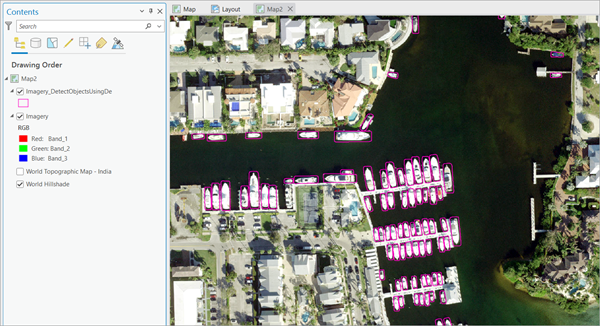
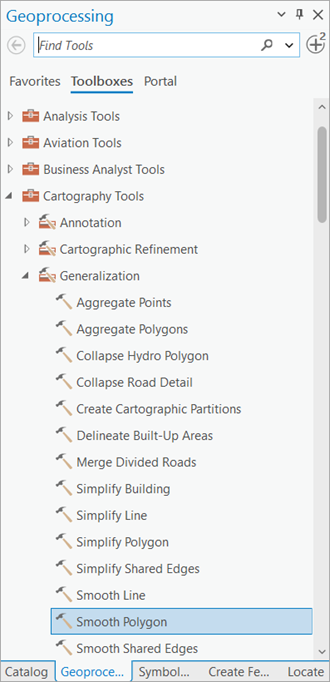
- Smooth the polygons using the following steps:
- Click the Toolboxes tab in the Geoprocessing pane, expand Cartography Tools, and browse to the Smooth Polygon tool under Generalization.
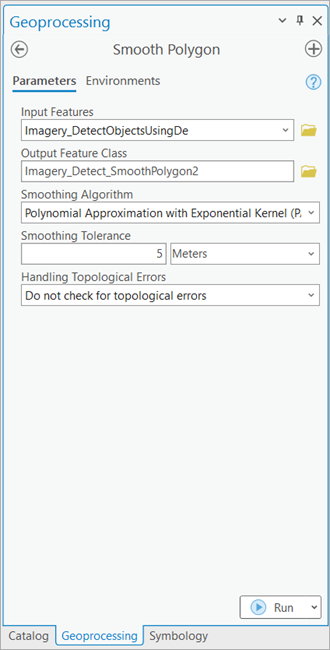
- Set the variables on the Parameters tab as follows:
- Input Features—Give the output of the Detect Object Using Deep Learning tool generated in previous steps as input here.
- Smoothing Tolerance—Specify the tolerance used by the Polynomial Approximation with Exponential Kernel (PAEK) algorithm.
It must be greater than zero. You can choose a preferred unit; the default is the feature unit.
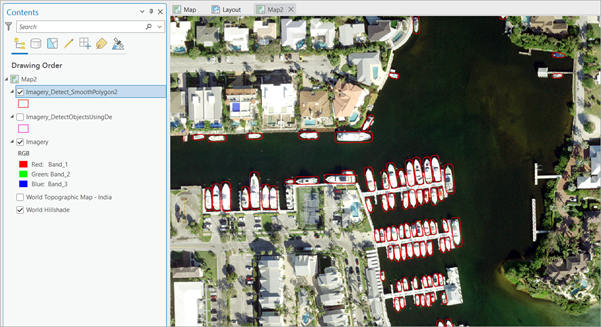
- Click Run
The output layer is added to the map.
- Click the Toolboxes tab in the Geoprocessing pane, expand Cartography Tools, and browse to the Smooth Polygon tool under Generalization.