


Attribute filters use queries to reduce the scope of the data you work with without changing the underlying data. Filters limit what you see on the page or card from one session to another session until you change or reset the filters. You can filter dates, numbers, rate/ratios, and string fields at the dataset level or for an individual card.
Example
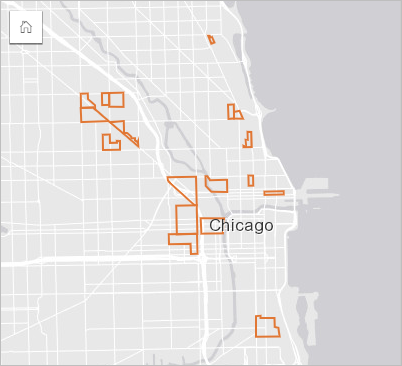
A retail chain is looking to expand into new markets in the Chicago area. Market research has shown that the chain's main clientele are women between the ages of 30 and 45 with a household income of at least $75,000. The market analyst has to use that information to determine the neighborhoods in which to expand.
The analyst has collected data for census block groups in Chicago, including total population, population of women by age range, and median household income. The analyst calculates a new field with the percentage of the total population that is women ages 30 to 45. With that preparation finished, the analyst is ready to apply filters and find which block groups fit the criteria of the market research.
The first filter is applied to the calculated field. After studying the distribution of the data, the analyst decides to set the threshold for percentage of women ages 30 to 45 to 20 percent. The second filter is created for the median household income, which the market research indicates should have a lower limit of $75,000.
In a few steps, the analyst narrowed down the data to the 18 best block groups for the new store locations. The analyst can now cross-reference the findings with zoning information and available retail rentals to find their final locations.
Filter types
An attribute filter can be applied to either the full dataset or a single card. Multiple filters can be applied to the same dataset and card. When multiple filters are applied to the same data, the filters are treated as if they are joined by an AND clause, meaning only features that match all filters are displayed.
Dataset filter
A dataset filter is applied to a field from the data pane and is reflected on all cards using the dataset, regardless of whether the filtered field is displayed on the card.
Complete the following steps to create a dataset filter:
- In the data pane, hover over the field you want to filter.
- Click the Dataset filter button
 next to the field.
next to the field. 
- Adjust the filter to include the data you want to show in the cards.
- Click Apply.
Card filter
A card filter is only applied to the data shown on a single card. Therefore, card filters can be used to make comparisons within a dataset by creating separate views of the same data.
After a card filter is applied, a number will be added to the Card filter button  showing the number of filters on the card. A result dataset
showing the number of filters on the card. A result dataset  will also be added to the data pane with the same filter applied to it at the dataset level. If new cards are created using the result dataset, all of the cards will reference the dataset filter on the result dataset, and the card filter will be removed from the original card. Since the original card also references the result dataset, there will be no change to the data being displayed.
will also be added to the data pane with the same filter applied to it at the dataset level. If new cards are created using the result dataset, all of the cards will reference the dataset filter on the result dataset, and the card filter will be removed from the original card. Since the original card also references the result dataset, there will be no change to the data being displayed.
Complete the following steps to create a card filter:
- Click the card you want to filter to activate it.
- Click the Card filter button
 .
. 
The Card filters pane appears.
- From the list, choose the field you want to filter.
Note:
If the card already has an existing filter, it will be listed in the Card filters pane. A new filter can be created by clicking New filter before choosing the field by which to filter.
- Adjust the filter to include the data you want to show in the cards.
- Click Apply.
Filter a number or rate/ratio field
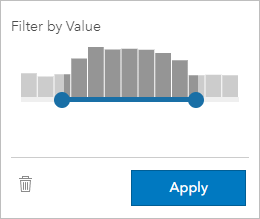
Numbers and rate/ratios are continuous data that is filtered by changing the range of values that are displayed. When you filter a number or a rate/ratio field, you see a histogram with a slider along the bottom. The histogram aggregates the values in the field into equal interval bins and displays the frequency of values within each bin. The histogram allows you to see how much data you're including or excluding with your filter.
Adjust the slider at the lower and upper ends of the range, or click the nodes and enter a new value.
Filter a string field
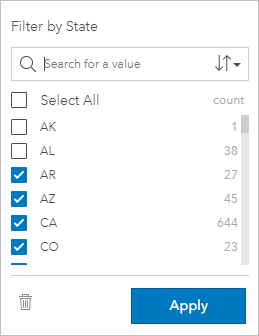
String fields contain text or, in some circumstances, discrete number values (for example, a ZIP Code is more accurately categorized as a string than as a number). When you filter a string field, you will select or deselect unique values that you want displayed or excluded. The following methods can be used to select or deselect values from a string filter:
- Select all—Turn on or off the Select All box to select or deselect all the values in the filter.
- Click—Turn on or off individual values in the filter. Only boxes that are clicked will be selected or deselected.
- Shift+click—Turn on or off multiple values. All boxes between the first and second click will be selected or deselected.
Note:
Shift+click can only be used on fields with fewer than 500 unique values.
Filter a date/time field
A date/time field contains temporal data. The following options are available depending on whether the date/time field contains dates only, times only, or dates and times:
- Dates only—Change the date range by using the calendar button to select start and end dates, adjusting the slider, or typing a date directly in the filter.
- Times only—Change the time range by using the clock button to select start and end times or typing the time directly in the filter.
- Dates and times—Change the date/time range by using the calendar and clock buttons to select a start and end date and time or typing the dates and times directly in the filter.
Tip:
An advanced filter can be used to incorporate date functions, such as DATEDIF() or NOW(), into your filter. See Create advanced filters for examples of expressions using dates and other functions.
A date/time field also contains subfields, such as Year and Month, which are stored and filtered as string fields.
Remove or update a filter
Attribute filters provide a specific view of your data and do not change the underlying data. Therefore, a filter can be edited or removed if it is no longer needed.
Tip:
If you plan on updating your filter frequently, you may want to use a cross filter, filter widget, or temporal filter widget instead of a regular attribute filter.
Update a dataset filter
Complete the following steps to update a dataset filter:
- Click the active Dataset filter button
 .
. - Do one of the following:
- Change the filter values and click Apply to update the filter.
- Click the Remove filter button
 to delete the filter. You can also select all filter values and click Apply to remove the filter.
to delete the filter. You can also select all filter values and click Apply to remove the filter.
Update a card filter
Complete the following steps to update a card filter:
- Click the active Card filter button
 .
. - Click the filter that you want to update.
- Do one of the following:
- Change the filter values and click Apply to update the filter.
- Click the Remove filter button
 to delete the filter. You can also select all filter values and click Apply to remove the filter.
to delete the filter. You can also select all filter values and click Apply to remove the filter.
Filter by n values
Note:
Top and bottom n values are currently available in card filters for bar charts, column charts, bubble charts, donut charts, and line charts. If you apply a filter by n values then switch to an unsupported visualization, the filter will be deleted.
Filtering using n values allows you to pick the top or bottom values on your chart based on its category and summary statistic.
Complete the following steps to filter by n values:
- Click the Card filter button
 on a supported chart type.
on a supported chart type. - Click the n values tab.
- Choose either Show top n values or Show bottom n values.
- Use the menu to choose a value for n, or type a number in the text box.
- Click Apply.
Cross filters
Cross filters are a way to filter your data using a selection on a different card. When the Enable cross filters button  is activated on a card, a filter will be applied to that card whenever a compatible selection is made. For a selection to be compatible, the card with the filter and the card with the selection must be using the same dataset.
is activated on a card, a filter will be applied to that card whenever a compatible selection is made. For a selection to be compatible, the card with the filter and the card with the selection must be using the same dataset.
Cross filters can be applied to all charts and tables. However, polynomial trendlines on scatter plots are not supported when using cross filters.
Limitations
Cross filters are not compatible with result datasets created from Buffer/Drive Times, Calculate Density, Calculate Density Ratio, Find Nearest, or Find Spatial Mean.
Filters by n values and cross filters are not available for certain remote feature layers.
If a filter is not supported for your layer, you can copy the layer to your workbook and apply the filter to the copy.
Resources
Use the following resources to learn more: