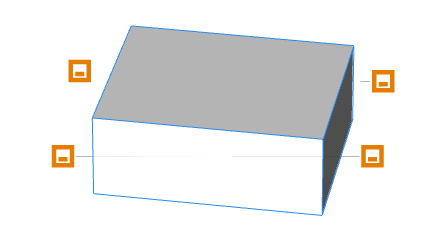
Handles are created by adding a @Handle annotation to an attribute.
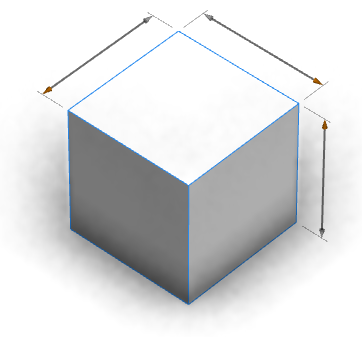
The above handles were created using the following attribute annotations:
@Handle(shape=Cube, axis=y)
attr height = 30
@Handle(shape=Cube, axis=x)
attr width = 30
@Handle(shape=Cube, axis=z)
attr depth = 30
Lot -->
s(width, 0, depth)
extrude(height)
CubeThe option shape=Cube attaches the handle to the shape Cube. The option axis=x|y|z specifies a scope direction for the handle. Thin gray extension lines connect the handle to the shape that it is measuring. Handles can be applied to a wide range of objects.
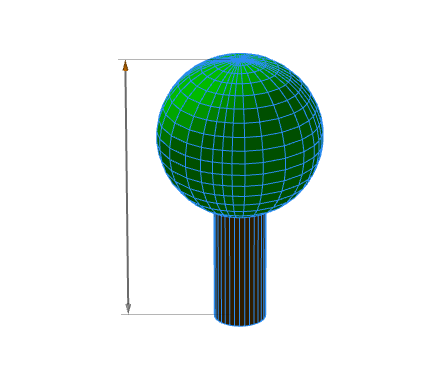
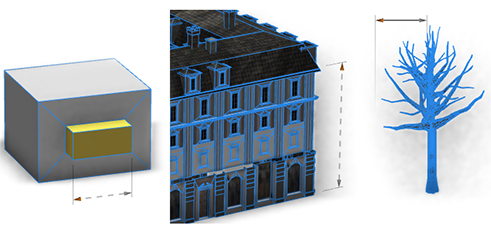
The above handle was created using the annotation:
@Handle(shape=TreeCenter, axis=y, reference=center, slip=screen)
attr height = 30Handles that do not move with the camera can also be created, for example:
@Handle(shape=TreeCenter, axis=y, reference=origin, slip=inside, occlusion=false)
attr height = 30The advanced options reference and slip specify the handle's position and movement as the camera moves. In this case the height handle rotates smoothly around the tree with the camera.
Note:
Adding many handles, or adding handles to complex models may lead to low framerates on low-end hardware.
General Options
The default options in the below table are marked with an asterisk. If any option is omitted, the default value is taken. The only option that must be specified is shape.
shape
shape=shape_name^argument_count |
Selects the shape of the rule with name shape_name. The parameter argument_count specifies the number of arguments that the rule takes. |
If ^argument_count is omitted, ^0 is assumed. An * allows referencing anonymous leaf shapes, e.g.: shape=Box*^3. |
type
type=linear*|move|angular|toggle|selector|color | |
Selects the type of handle to create. , and color for editing color string attributes. | |
Additional options specific to each type are given below: | |
type=linear Handles with a linear type are used for editing float values that represent distances. |  |
type=move The move type is used for editing float values that represent positions, in contrast to the linear type the handles are always shown at a constant length. |  |
type=angular The angular type is for float attributes that represent angles. | 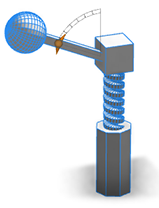 |
type=toggle The toggle type is for boolean attributes. |  |
type=selector The selector type is for attributes with the @Enum annotation. | 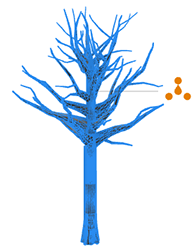 |
type=color The color type is for editing color string attributes. | 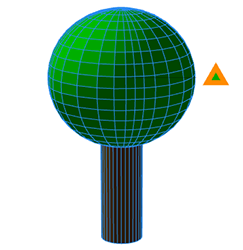 |
align
align=topLeft|left|bottomLeft|bottom|bottomRight|right|topRight|top|default* | |
Selects a screen direction as the offset direction preference for a reference handle. default selects the nearest location outside of the model's silhouette. | |
linear example of align=left | 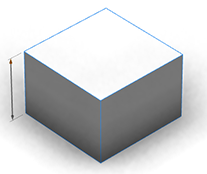 |
linear example of align=right | 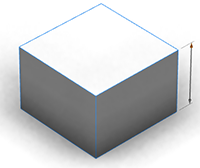 |
toggle example of align=topLeft |  |
toggle example of align=right |  |
slip
slip=scope*|screen|inside |
This option specifies the way in which reference handles may be moved outside the model's silhouette. slip=scope moves the handle in directions given by the scope axes, slip=screen moves the handle parallel to the camera, and slip=inside disables the offsetting behvior. |
Different slip are appropriate for different shapes. For example, the length of cylindrical objects is best specified using slip=screen, while the dimensions of a cuboid should use slip=scope. |
In the below image we see that slip=scope causes the handle to align itself to the edges of the scope as the camera moves. In contrast slip=screen maintains a constant offset direction, independent of camera location. |
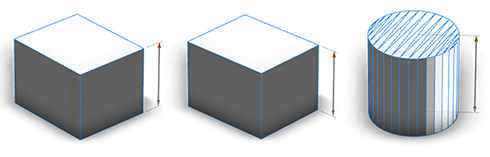 |
It is recommended that cuboid objects use slip=scope, while cylindrical or spherical objects will use slip=screen. While it is possible to use either of these options in any case, following these recommendations presents a consistent and intuitive interface to users. |
repeat
repeat=chain*|none |
Chained handles will be clustered into a single continuous chain. Linear handles of several different attributes with the same orientation may be grouped onto one chain if there is sufficient space. |
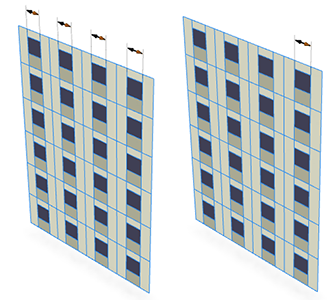 |
If repeat=none is set, CityEngine determines an appropriate location for a single handle, preferring locations with short extension lines and long linear handles. |
minDisplaySize
minDisplaySize=pixels |
If the size of a handle is below pixels, it is not shown. Users can override this behavior by pressing the command key (Mac) or control (PC / Linux). |
The size of a handle with linear type is the screen-length. The size of an angular handle is the distance between zero degree and the handle. The size of toggle, selector, or color handles is the screen length of the shape's scope's shortest edge. |
extensionLines
extensionLines=scope*|silhouette|fade|off |
Specifies the style of the extension lines associated with a handle. |
 |
The image below shows typical use cases for the different extension line types. scope (left) is used to highlight embedded features, silhouette (middle) with obvious features to avoid cluttering the geometry and fade (right) for irregular shapes. |
 |
translate
translate={translate_x,translate_y,translate_z} |
Specifies a scope-relative translation of the handle. For example, translate={3,0,0} translates the handle by 3 * scope.sx in the direction of the scope's x axis. |
occlusion
occlusion=true*|false |
Enables or disables occlusion handling for the handle. When enabled handles are only shown when their reference positions are visible. However, for complex models this may cause the handle to flicker. Using occlusion=false will resolve this issue, and never hide the handle because of occlusion. |
color
color=hexCodeString |
Normally the color of handles is given by the viewport hightlight color. color allows users to override this behavior with a preferred color hexCodeString is specified as an RGB hex code string within quotes, for example color="#FF0000". |
 |
Linear Type Options
Linear handles are assumed to be associated with a scope edge. The length of the linear handle is given by the scope edge specified by axis.
reference
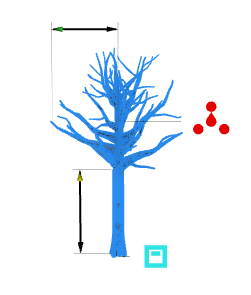
reference=edges*|center|origin|radial | |
Specifies the location of the reference handles. Note:The location of radial handles depends on the camera position. | |
Handles are moved to their offset position using the direction given by the slip option. | |
| reference=edges Typical use cases are boxes or cuboid geometries (as shown in the first example on this page). | 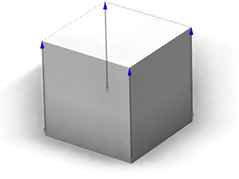 |
| reference=center Suitable for the length of cylindrical or spherical objects (such as the tree's height in the second example of this page). | 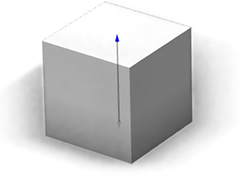 |
| reference=origin Used when a feature is one dimensional or when the exact position of a handle must be specified. The shape's origin is at the right of the cube. | 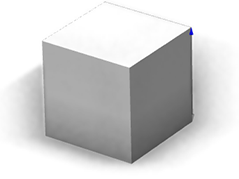 |
| reference=radial Can be used for the width of cylindrical objects (such as the dead tree model above). | 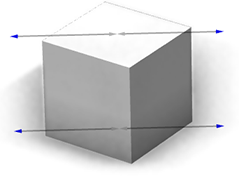 |
axis
axis=y*|x|z|x-|y-|z- |
The linear handle is positioned along the specified scope axis of the shape. |
skin
skin=doubleArrow*|singleArrow|diameterArrow|sphere|hemisphere | |
Linear handles have several options for the rendering of terminators. These options do no change the behavior of the handle, with the exception of skin=diameterArrow, which scales symmetrically about its center when dragged. | |
| skin=doubleArrow | 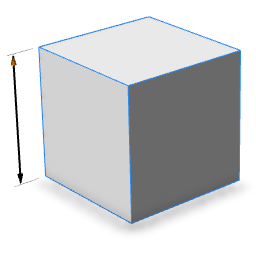 |
| skin=singleArrow | 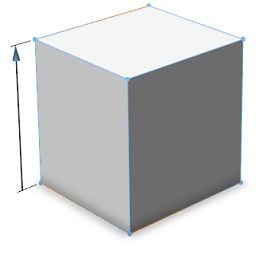 |
| skin=diameterArrow | 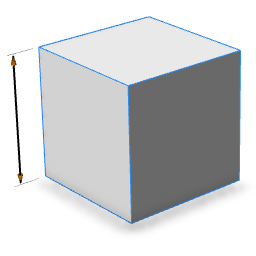 |
| skin=sphere | 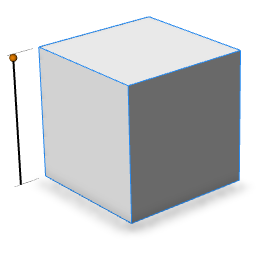 |
| skin=hemisphere | 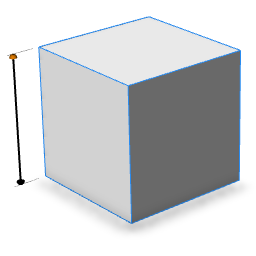 |
Move Type Options
Move handles are similar to linear handles, and are also associated with a scope edge. However, the length of the move handle is always constant, in contrast to linear handles where it is given by the scope edge. When dragging one end of the handle, the other end also moves by the same amount. This makes them suitable for attributes representing positions or offsets.
axis and skin are similar to linear handles. For reference, only center and origin is supported. Also, the slip value is restricted to inside.
Angular Type Options
Angular handles allow the user to manipulate angles. Typically a combination of axis and translate are used to position the handle in the appropriate location. By default, angular handles do not offset themselves (slip=inside). This behavior can be altered by specifying another slip value.
reference
reference=edges|center*|origin | |
Specifies the location of the reference handles. In the below images, the shape origin is in the bottom right of the screen. | |
| reference=edges |  |
| reference=center |  |
| reference=origin |  |
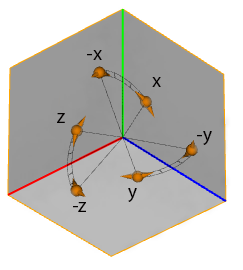
axis
axis=y*|x|z|x-|y-|z- |
Selects the rotation scope axis.. A negative axis reverses the direction of rotation. |
 |
skin
skin=doubleArrow*|ring | |
Rotational handles have two skin options: doubleArrow or ring. | |
| skin=doubleArrow | 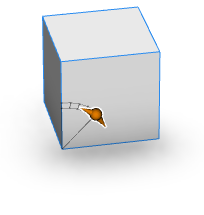 |
| skin=ring | 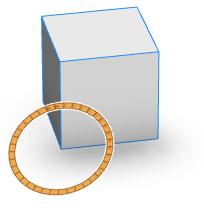 |
Toggle, Selector and Color Type Options
Toggle, selector and color types share layout options.
reference
reference=edges|center*|origin|radial | |
Specifies the location of the reference handles. In the below images, the shape origin is in the bottom right of the screen. Note:The location of radial handles depends on the camera position. | |
| reference=edges | 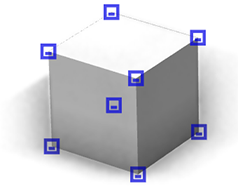 |
| reference=center |  |
| reference=origin |  |
| reference=radial | 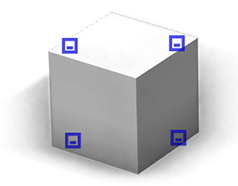 |
axis
| if slip=scope |
axis=x|y*|z|xy|xz|yz |
Specifies the directions in which the handle may move when slip=scope is set. For example, handles with the option axis=xy may move along the x or y axes. |
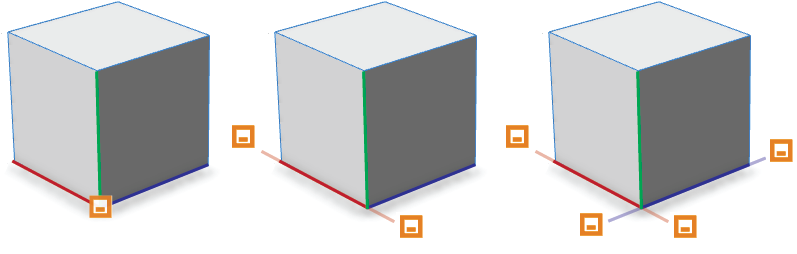 |
if slip=screen |
axis=x|y*|z |
In the case of slip=screen the handle moves in the same manner as a linear handle with the same axis parameter. |
if slip=inside |
axis does not affect the placement of the handle if slip=inside. |