Intersection Parameters can be individually set for each graph node.
The parameters for Intersection Shape creation can be specified through the Intersection Parameters pane in the Inspector.
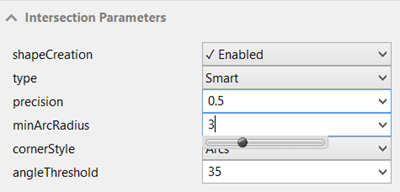
Several parameters are available for the user to control the resulting intersection shapes. Intersection parameters define the type of the intersection (crossing, junction, roundabout, freeway or smart) and specify geometry details like the radius of the arcs for instance.
Note:
Attributes can be mapped to Default, User, Object or to a map layer. See Mapping Attributes for details.
General parameters
shapeCreation | If true, shapes are created from the graph node. |
type | |
Specifies the type of the intersection. Crossing, junction, roundabout or freeway. Smart automatically chooses between these types. | |
Crossing | 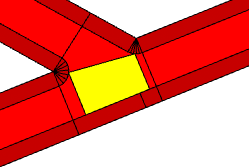 |
Junction | 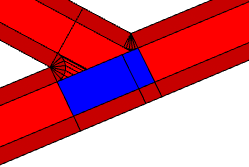 |
Roundabout | 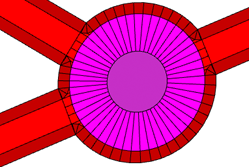 |
Freeway | 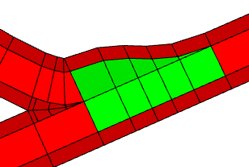 |
Common parameters
precision | |
Specifies the level of detail. Value must be in the range [0, 1]. | |
Crossing shapes with precision = 0.1. | 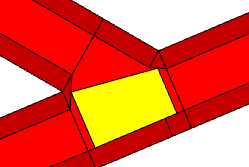 |
Crossing shapes with precision = 0.3. | 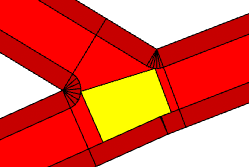 |
minArcRadius | |
The minimal arc radius. For freeways a higher value (>20) is better suited. | |
Given in absolute length units. | |
Crossing shapes with minArcRadius = 0. | 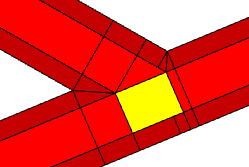 |
Crossing shapes with minArcRadius = 5. | 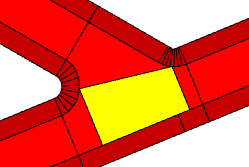 |
angleThreshold | |
Minimum angle between streets before they automatically start bending to avoid each other. It is ignored for freeways. | |
Crossing with angleThreshold set to 30. Note the streets bending to avoid each other. | 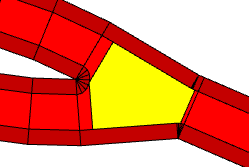 |
Crossing with angleThreshold set to 10. | 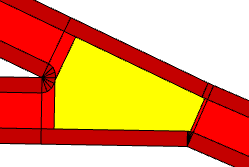 |
Crossing and junction parameters
In addition to the above parameters, crossing and junction creation has the following parameter:
cornerStyle | |
Either Arcs or Straight. When set to the latter, blocks get simpler. | |
Border with cornerStyle set to Arcs. | 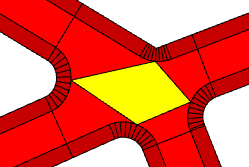 |
Border with cornerStyle set to Straight. | 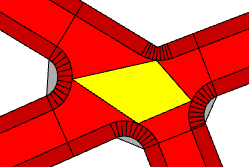 |
Roundabout parameters
In addition to the general parameters, roundabout creation uses the following values:

innerRadius | Defines the radius of the inner circle (the "island shape"). |
streetWidth | |
Defines the width of the roundabout street lane. | |
A roundabout with innerRadius = 5 and streetWidth = 10. | 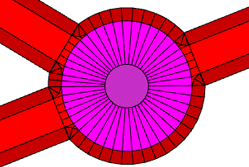 |
A roundabout with innerRadius = 10 and streetWidth = 5. | 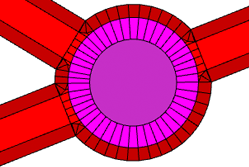 |
Principle street selection
The junction and freeway intersection types make use of the principle street to determine the intersection geometry. The principle street does not alter the smart junction behavior.
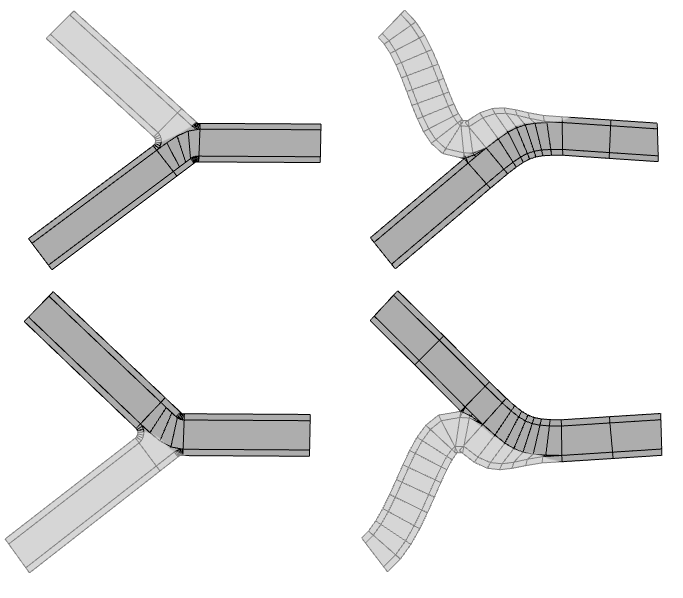
Note:
The principle street is specified using either the street tool, or by setting the object attribute principleStreetStart or principleStreetEnd on adjacent streets as appropriate.
Examples
Simple curve
Valence-two nodes (nodes between 2 graph segments) usually lead to curves or links between the segments.
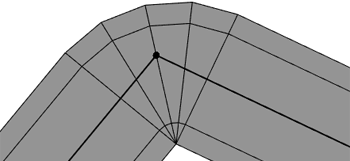
Note:
For valence-one (nodes at the end of a row of segments / cul-de-sac) or valence-two nodes it does not matter whether the type is crossing or junction.
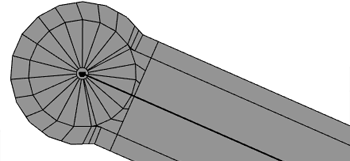
Dead end street
By setting the type of a valence-one node to roundabout, one can model a cul-de-sac.
Junction
Junctions, as opposed to crossings, don't break a major street. Minor streets are connected to the major street by junction entries.
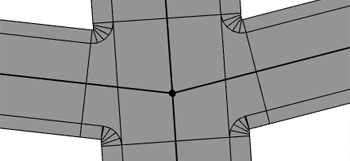
Note:
The two segments with the maximal street widths are automatically treated as major street.
Auto-generated connection attributes
Connection attributes provide basic information about the underlying graph and give context information. CGA rules may want to access the following attributes.
valency | The number of street segments adjacent to a street node. Valency is added to all intersection shapes. |
sidewalkSide | Which side of the street this Sidewalk shape is on, relative to the street direction: either Left or Right. SidewalkSide is only added to Sidewalk shapes. |
Note:
Connection attributes are object attributes of the graph node and are inherited to the shape, indicated by the italic font in the shape's Inspector.