This lesson builds on the Create a feed lesson in which you created a new feed to collect Automatic Identification System (AIS) ship data. It demonstrates how to create a real-time analytic on streaming data in Velocity by configuring a real-time analytic to enrich the streaming AIS data with the U.S. Coast Guard district where each ship is located. The lesson covers adding and configuring real-time tools, adding outputs that disseminate data, and storing features in a feature layer.
This lesson is designed for beginners. You must connect to an ArcGIS organization with access to ArcGIS Velocity. The estimated time to complete this lesson is 30 minutes.
Create a new real-time analytic
To begin, create a real-time analytic on the AIS feed that was created in the Create a feed lesson.
- In a web browser, open ArcGIS Velocity and sign in with your ArcGIS Online credentials.
Google Chrome or Mozilla Firefox is recommended.
Note:
If you encounter issues signing in, contact your ArcGIS organization administrator. You need to be assigned a role with privileges to use Velocity.
- From the main menu, under Analytics, click Real-Time to access the Real-Time Analytics page.
Tip:
The Getting Started section on the Home page has a Create real-time analytic shortcut button under Real-Time Analytic.
On the Real-Time Analytics page, you can perform the following actions on existing real-time analytics:
- Review
- Create
- Start
- Stop
- Check status
- Edit
- Clone
- Delete
- Share
- View logs
- Check metrics
- Click Create real-time analytic to open the analytic configuration wizard.
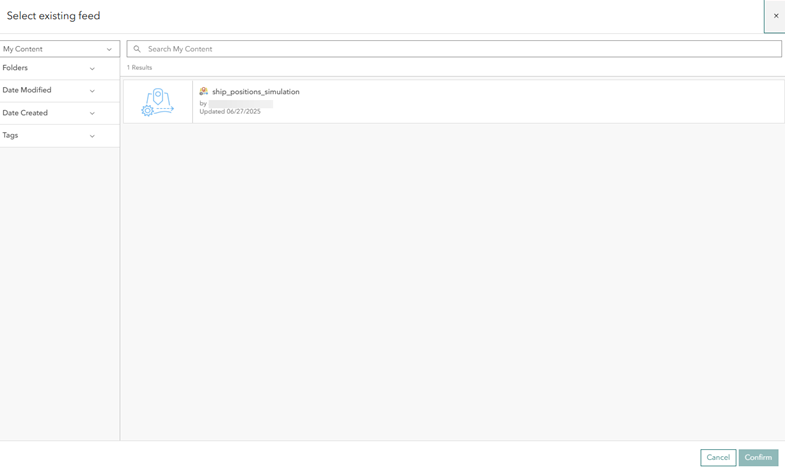
- On the Create a new real-time analytic page, click Existing feed.

- On the Select existing feed dialog box, choose the ship_positions_simulation feed and click Confirm.
Note:
The ship_positions_simulation feed is available if you completed the Create a feed lesson. If it is not available, complete that lesson before continuing.
The real-time analytic editor appears, where you can configure additional tools and outputs. By default, the editor shows the chosen feed and all processing elements in a linear, sequential layout.

Create the analytic
Although the analytic only contains the input feed at this point, you create it so you can return to it later if necessary.
- On the New Real-Time Analytic page, click Create analytic.
The Create Analytic dialog box appears.
- Set the Title and Summary parameters as follows:
- For Title, type AIS Real Time Processing.
- For Summary, type Filter and modify incoming AIS data with streaming output and feature storage.
- For Folder, choose the folder where you want to save the new analytic.
- Click Create analytic to create the analytic.

The analytic editor appears, where you can add new elements including feeds, sources, analytic tools, and outputs.

Add and configure an analytic tool
Next, add a tool to the AIS Real Time Processing analytic to perform real-time analysis on the AIS data feed. With Velocity, you can build a sequence of successive analytic nodes that define the flow of data from inputs to outputs.
Use the Join Features tool to enrich the inbound AIS data with the name of the U.S. Coast Guard district where each ship is located. The tool performs a spatial join between the ship point features and the U.S. Coast Guard District polygon layer.
- Add the Join Features tool to the AIS Real Time Processing analytic and connect it to the ship_positions_simulation feed.
- From the Add Node menu, click Summarize Data.
- Drag the Join Features tool node next to the ship_positions_simulation feed node.
- Connect the ship_positions_simulation feed node to the Join Features tool node.

- Click Sources, choose Feature Layer and configure the feature layer source as follows:
- Click the My Content drop-down menu and choose By URL.
- In the Layer URL text box, type https://services2.arcgis.com/FiaPA4ga0iQKduv3/arcgis/rest/services/US_Coast_Guard_Districts_new/FeatureServer.
- Choose the USCG_Districts (0) sublayer and click Next.

- For Filter Data, set the Output spatial reference (optional) parameter to GCS WGS 1984 and click Next.
- For Confirm Schema, accept the schema as sampled and click Next.
Velocity samples the data and generates a schema to start with.
- For Identify Key Fields, under Tracking, choose Data does not have a Track ID.
This step of the configuration wizard is used to define the construction of geometry, date and time, and tracking information. Since the data source is an ArcGIS feature layer, the geometry and date and time information is automatically configured.
- Click Complete to create and add the data source to the editor.
- Drag the USCG_Districts source node below the ship_positions_simulation feed node and connect it to the Join Features tool node.

The U.S. Coast Guard District feature layer is added as the enrichment data source to the Join Features tool. The Join Features tool now has two inputs connected to it: the ship positions feed and the U.S. Coast Guard District feature layer data source.
- Double-click the Join Features tool to open its properties and configure the tool as follows:
- For Join operation, click One-to-one.
- For Retain all features, click Only retain features that are joined.
- For Relationship, check the Spatial check box and choose Intersects from the drop-down menu for the spatial relationship type.
- Set the Summary fields parameters.
- For Attribute, choose DistrictName.
- For Statistic, choose Any.
The default is Any.
- For Output field name, delete DistrictName_Any and type DistrictName.
- Click Update summary fields to save the properties.
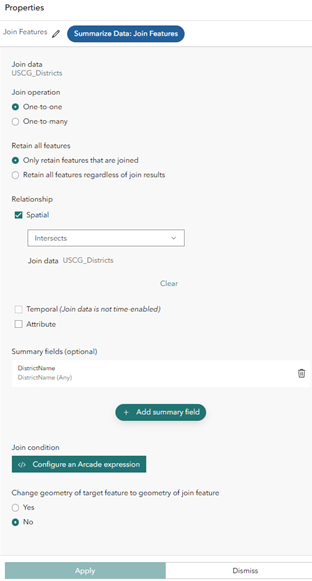
- Leave Change geometry of target feature to geometry of join feature set to No.
- Click Apply to save the properties.
- In the analytic editor, click Save to save the AIS Real Time Processing analytic.
This lesson demonstrates how to detect ships that intersect a U.S. Coast Guard district, and how to add, or join, that contextual information to the ship data. This can be used for increased situational awareness or further analysis.
Configure a feature layer output
With the data source and analytic tools created, you can add two outputs to store and visualize the data. First, add and configure an output to store the data in a new feature layer. Then, add another output to send the data to a stream layer for visualization in a web map.
Note:
The spatiotemporal feature layer name must be unique within an organization.
In Velocity, the spatiotemporal feature layer name must be different from the feed and stream layer names. If there is a duplicate name, you cannot create a real-time or big data analytic in Velocity. This only applies to Velocity feature layer outputs; it does not apply to ArcGIS Online hosted feature layers.
To add an output, complete the following steps:
- From the Add Node menu, click Outputs and choose Feature Layer (new) and configure the output as follows:
- For Data storage method, choose Keep only latest feature for each Track ID value.
This retains only the latest observation for each track, in this case each ship. Subsequent observations overwrite any previous observations for each track in the output feature layer.
Note:
The Add all new features option retains all incoming data rather than only the most recently received features.
- For Each time the analytic starts, choose Replace existing features and schema.

Each time the analytic starts, all records in the output feature layer are deleted and the schema of the output feature layer is regenerated. This is useful for developing and testing a real-time analytic and adding, removing, or changing tools between analytic runs.
Note:
Choose the Keep existing features and schema option to retain the existing data when the real-time analytic restarts.
- Click Next.
- For Save, for Feature layer name, type Ships_Inside_USCG_Districts.
- For Feature layer summary (optional), type Ships inside US Coast Guard Districts.
- For Folder, choose the folder to save the feature layer.
- Click Complete to save the new feature layer output.

The new feature layer output, Ships_Inside_USCG_Districts, is added to the analytic editor.
- For Data storage method, choose Keep only latest feature for each Track ID value.
- Connect the Join Features tool node to the new Ships_Inside_USCG_Districts feature layer output node.

- Click Save to save the real-time analytic.
Configure a stream layer output
With the new feature layer output added and the real-time analytic saved, add a second output to send the features to a stream layer that you can visualize in a web map.
Note:
The stream layer name must be unique within an organization.
In Velocity, the stream layer name must be different from the feed and spatiotemporal feature layer names. If there is a duplicate name, you cannot create a real-time or big data analytic in Velocity.
- From the Add Node menu, click Outputs, choose Stream Layer, and configure the output as follows:
- For Stream Layer Configuration, click Next to accept the default parameters.
The Also publish a feature layer which keeps the latest observation for each Track ID and Select a related feature layer to provide geometry when stream layer is drawn in a map parameters are not required. When you publish a feature layer, you can publish a separate feature layer that contains only the latest observations. This is useful when you want to symbolize the active position of an asset, in this case a ship, differently in a web map. You can choose a related feature layer that can be used to enrich the output stream layer with additional fields.
- For Stream layer name, type Ships_Inside_USCG_Districts_stream.
- For Stream layer summary (optional), type Ships inside USCG Districts stream.
- For Folder, choose the folder to save the stream layer.

- For Stream Layer Configuration, click Next to accept the default parameters.
- Click Complete to create the stream layer output.
The new stream layer output, Ships_Inside_USCG_Districts_stream, is added to the analytic editor.
- Connect the Join Features tool node to the Ships_Inside_USCG_Districts_stream stream layer output node.

- Click Save to save the real-time analytic.
Start the real-time analytic
The real-time analytic includes the necessary feed, data source, tool, and outputs and is ready to be started. When started, or running, the analytic receives the simulated ship data, joins it to the name of the U.S. Coast Guard district where each ship is currently located, and writes the event data to the feature layer and stream layer outputs.
- In the analytic editor, click Start.
As with feeds, real-time analytics are long-running tasks and continue to run until they are stopped.
The Start button becomes a Stop Initialization and then a Stop button, indicating that the analytic has started and is running.
- View the status and monitor the AIS Real Time Processing analytic on the Real-Time Analytics page.
View the real-time analytic metrics
The real-time analytic metrics can be viewed in Velocity. Metrics provide the average rate of events through each element and represent an average rate for each element for the past five minutes of run time. While a real-time analytic is running, the metrics represent the compute usage of the analytic.
Learn more about real-time analytic metrics
- In the AIS Real Time Processing real-time analytic, click the Metrics toggle button
to view metrics for each node in the analytic.
- Review the metrics for each node in the real-time analytic. Notice the events per second that each node is processing, the total number of observations in and out, and the compute usage.

Examine the output layer
With the real-time analytic running and sending event data to the feature and stream layer outputs, you can add these output layers to a web map directly in the real-time analytic.
- From the main menu, under Input, click Feeds to access the Feeds page.
- If the ship_positions_simulation feed is not already started, click Start.
- From the main menu, under Analytics, click Real-Time to access the Real-Time Analytics page.
- If the AIS Real Time Processing real-time analytic is not already started, click Start.
- Once the AIS Real Time Processing real-time analytic is running, click the Edit button to edit the analytic.
- Right-click the Ships_Inside_USCG_Districts feature layer output and choose Open in Map Viewer.

A new browser tab opens Map Viewer in the ArcGIS organization and adds the feature layer to the web map.
- Change the basemap to Dark Gray Canvas.

- Click Add and choose Add Layer from Web.
- Add the U.S. Coast Guard Districts feature layer using the URL https://services2.arcgis.com/FiaPA4ga0iQKduv3/arcgis/rest/services/US_Coast_Guard_Districts_new/FeatureServer.

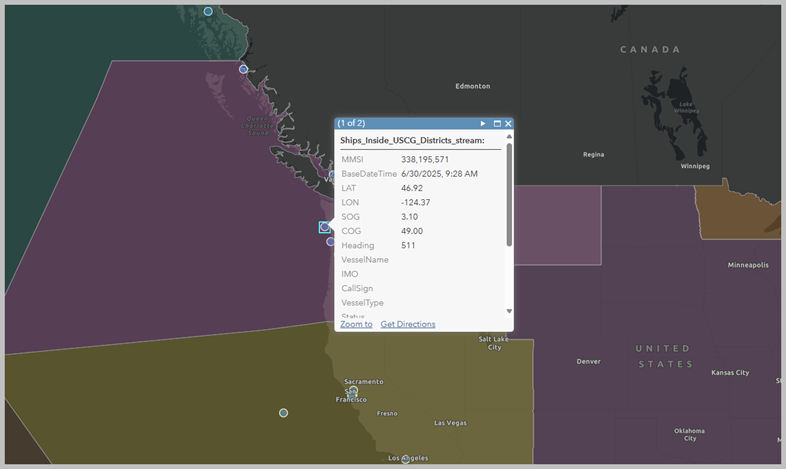
- Click one of the ship features to open the pop-up and explore its attributes.
Each observation is enriched with the name of the U.S. Coast Guard district (DistrictName) that the ship is currently in.
Next steps
You created a real-time analytic using Velocity and viewed the output features in a web map. Then you added the Join Features tool to perform spatial enrichment and associated contextual information with the ingested observation data.
Next, explore the Design a big data analytic lesson that introduces you to working with big data analytics in Velocity. If you are interested in using Arcade expressions, refer to Arcade expressions.