ArcGIS Arcade is a portable, lightweight, and secure expression language that can perform mathematical calculations, manipulate text, and evaluate logical statements. It also supports multi-statement expressions, variables, and flow control statements. What makes Arcade particularly unique to other expression and scripting languages is its inclusion of feature and geometry data types. A common use case for Arcade is to perform a calculation with layer fields and geometry.
Usage notes
Keep the following in mind when using Arcade expressions:
- Arcade expressions are supported in the Detect Incidents, Calculate Field, Filter by Expression, Map Fields, Join Features, Create Buffers, and Reconstruct Tracks tools.
- Expressions can incorporate attributes from input feed types and source types as well as values that describe the analytic in which the expression is configured.
- In the expression builder, the profile variables can be expanded to display a list of fields, time values, target fields, and join fields. ArcGIS Velocity expressions use the following profile variables:
- $feature—In all tools, except Join Features, this variable contains the attribute fields of the incoming features from feeds and sources. Expressions that use feature attribute values can be built by selecting fields from this variable.
- $analytic—This variable contains values specific to the analytic such as $analytic.AnalyticStartTime and $analytic.AnalyticLastEndTime.
- To convert these analytic variable values from an epoch integer (1646409900000) to a date, use the Arcade Date() function. For more information, refer to date functions in the Arcade documentation.
- $target—In the Join Features tool, for the Join Condition expression, this profile variable contains the attribute fields from the target feed or source.
- $join—In the Join Features tool, for the Join Condition expression, this profile variable contains the attribute fields from the join source.
- Access fields and schema components in the Arcade expression builder.
- From the Profile variables pane, access fields, variables, and components of the schema related to the category, for example, $feature, $analytic, $target, or $join.
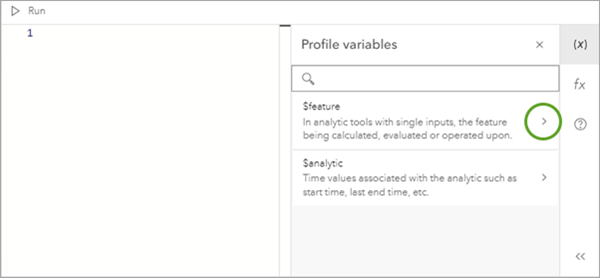
- This displays the fields or variables related to that variable.
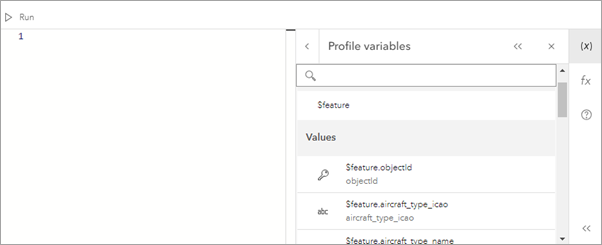
- From the Profile variables pane, access fields, variables, and components of the schema related to the category, for example, $feature, $analytic, $target, or $join.
- Provide your own sample values for Arcade expression testing.
- Arcade provides default sampled values for each tool depending on the incoming schema. You can update the sampled values while building the expressions for each tool.
- To adjust sample values for Arcade expression testing, do the following:
- Based on the incoming schema, if you click to edit an Arcade expression, the Configure an Arcade expression dialog box opens.
- On the $feature tab, notice that for each incoming field, there is a sampled value displayed based on its data type. For example, every string field has a sample value of Pacific. To build and test a valid expression for different datasets, you must change the sampled values provided for a field so the Arcade expression evaluates the expression and returns the correct data type returned by the expression.
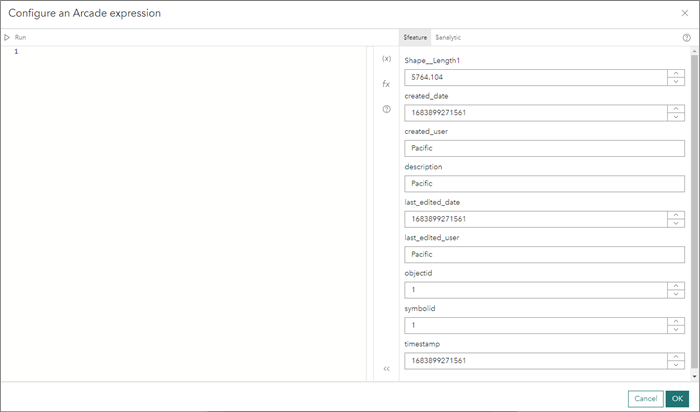
- Adjust the sampled value if used in Arcade expression testing and evaluation.
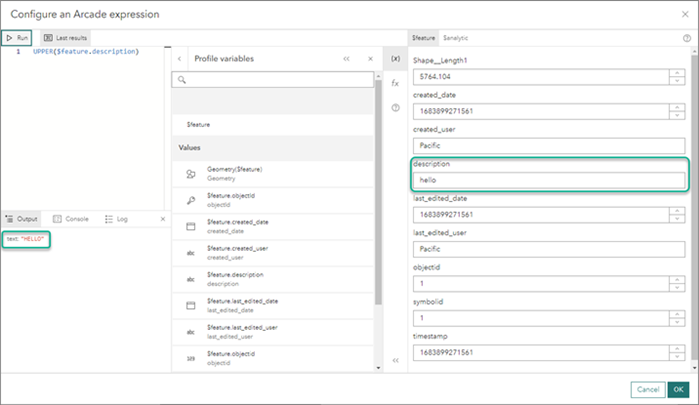
- Click Run in Configure an Arcade expression dialog box to run the Arcade expression. The expression evaluates based on the updated sampled data provided.
- Build Arcade expressions to handle null and 0 values.
- In mathematic operations, the Arcade expression language treats null values as 0 for evaluation. Therefore, Arcade mathematical expressions in Velocity should be created to account for null values in your data.
- Account for null values in your data by handling null values. Consider the expression $feature.DistanceToFeature <= 5. This expression should be built in the Arcade language to handle nulls such as $feature.DistanceToFeature != null && $feature.DistanceToFeature <= 5. In these expressions, the <= 5 is a mathematic operation and if the DistanceToFeature field value is null, it is evaluated as 0, which would pass the expression.
Mathematical operator and function examples
Expressions can mathematically process numbers. The table below provides a sample of available operations.
Learn more about mathematical operations in Arcade
| Operator | Syntax | Explanation | Example | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Addition | a + b | a plus b. | fieldname contains a value of 1.5 $target["fieldname"] + 2.5 | 4.0 |
Subtraction | a - b | a minus b. | fieldname contains a value of 3.3 $target["fieldname"]- 2.2 | 1.1 |
Multiplication | a * b | a times b. | fieldname contains a value of 2.0 $join["fieldname"] * 2.2 | 4.4 |
Division | a / b | a divided by b. | fieldname contains a value of 4.0 $join["fieldname"] / 1.25 | 3.2 |
Absolute value | abs( a ) | Returns the absolute (positive) value of a. | fieldname contains a value of -1.5 abs($target["fieldname"]) | 1.5 |
Logarithm | log( a ) | Returns the natural logarithm (base E) of a. | fieldname contains a value of 1 log($join["fieldname"]) | 0 |
Sine | sin( a ) | Returns the trigonometric sine of a. The input is assumed to be an angle in radians. | fieldname contains a value of 1.5707 sin($target["fieldname"]) | 1 |
Cosine | cos( a ) | Returns the trigonometric cosine of a. The input is assumed to be an angle in radians. | fieldname contains a value of 0 cos($join["fieldname"]) | 1 |
Tangent | tan( a ) | Returns the tangent of a. The input is assumed to be an angle in radians. | fieldname contains a value of 0 tan($target["fieldname"]) | 0 |
Square root | sqrt( a ) | Returns the square root of a. | fieldname contains a value of 9 sqrt($join["fieldname"]) | 3 |
Minimum | min( a, b ) | Returns the number between a and b with the lowest value. | fieldname contains a value of 1.5 and a value of -3 min($join["fieldname"], -3) | -3 |
Maximum | max( a, b ) | Returns the number between a or b with the highest value. | fieldname1 contains a value of 1.5 and fieldname2 contains a value of -3 max($target["fieldname1"], $join["fieldname2"]) | 1.5 |
Constraint | constrain(<value>,<low>,<high>) | Returns the input value if it is within the constraining bounds. If the input value is less than the low value, it returns the low value. If the input value is greater than the high value, it returns the high value. | constrain($target["distance"], 0, 10) constrain($join['Store dist'], 6, distance) | Returns 0 if distance is less than 0; 10 if distance is greater than 10; and distance otherwise. Returns 6 if Store dist is less than 6; distance if Store dist is greater than distance; and Store dist otherwise. |
The following multiplication example for a join condition expression uses a field from the target dataset:
$target["Distance"] * 2 > $join["DistField"]
Text function examples
Arcade expressions can process text. The table below provides a sample of available operations.
Learn more about text functions in Arcade
| Function | Syntax | Explanation | Example | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Concatenation | concatenate(<values>, <separator>) | Concatenates values together and returns a string.
| fieldname contains a value of Velocity concatenate([$target["fieldname"], "is", "great!"], ' ') | Velocity is great! |
Find | find(<searchText>, <text>, <startPos>) | Finds a string in a string. Wildcards are not supported.
| fieldname1 contains a value of 14NorthStreet and fieldname2 contains a value of North find($target["fieldname2"], $join["fieldname1"]) | 2 |
Lowercase | lower(<value>) | Makes a string lowercase.
| fieldname contains a value of ANALYTICS lower($join["fieldname"]) | analytics |
You can combine text functions to perform a complex operation. The following text function example uses the find and lower functions:
find(("north"), lower("146NorthStreet")) == False
Date function examples
Arcade can process dates. In Arcade, month values range from 0 (January) to 11 (December); days from 1 to 31; hours from 0 (12:00 a.m.) to 23 (11:00 p.m.); minutes and seconds from 0 to 59; and milliseconds from 0 to 999.
The following table provides a sample of available operations:
Learn more about date functions in Arcade
| Function | Syntax | Explanation | Example | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Date creation | date( <value>, <month>, <day>, <hour>, <minute>) | Parses a value, or set of values, into a date string.
| fieldname contains a value of 1476987783555 Example 1: Date($target["fieldname"]) Example 2: Date(2017,0,14,0) Example 3: Date() | Example 1: 20 Oct 2016 11:23:03 am Example 2: 14 Jan 2017 12:00:00 am Example 3: Returns the current time |
Date difference | DateDiff(<date1>, <date2>, <units>) | Subtracts two dates and returns the difference in the specified units.
| Example 1: DateDiff(Date(2017,1,14,0), Date()) Example 2: DateDiff(Date(2017,1,14,0), Date(), "Years") | Result varies depending on when the command is run. Example 1: -20532129137 Example 2: -0.6546783768647119 |
Year | Year(<dateValue>) | Returns the year of the given date.
| Example 1: fieldname is a field of type Date with a value of value of 09 Oct 2017 04:30:43 pm Year($join["fieldname"]) Example 2: fieldname is a string field formatted as an ISO 8601 string with a value of 2012-09-27 Example 3: fieldname is a string field formatted as an ISO 8601 string with a value of Year(Date($target["fieldname"])) | Example 1: 2017 Example 2: 2012 |
Conditional operators
Conditional statements can use the following operators:
| Operator | Syntax | Explanation | Example | Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Relational or Comparison | a > b a < b | a is greater than b. a is less than b. | 10 > 2 | False |
a >= b a <= b | a is greater than or equal to b. a is less than or equal to b. | abs(-10) >= 10 | True | |
a != b | a is not equal to b. | abs(-3) != -3 | True | |
a == b | a is equal to b. | abs(-5) == 5 | True | |
Logical OR | <condition1> || <condition2> | Condition 1 or condition 2 is met. | (abs(-5) == 5) || (10 < 2) | True |
Logical OR | <condition1> && <condition2> | Condition 1 and condition 2 are met. | (abs(-5) == 5) && (10 < 2) | False |
The following example of a buffer expression uses advanced functions and conditions:
iif(field1 > field2, iif(field2 = 0, field3, field4), 0)
The following is a multiplication example for a join condition:
iif(field1 > field2, iif(field2 = 0, field3, field4), 0) > $join["Distance"] * 2
Logical operator examples
In addition to the conditional operators, advanced logical operators can be used to create expressions. The following table includes examples:
Learn more about logical functions in Arcade
| Function | Syntax | Explanation | Example | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|
IIf | iif(<condition>,<true value>,<false value>) | Returns one value if a condition evaluates to true and returns another value if that condition evaluates to false. <true value> and <false value> can be the following:
| iif($feature["field1"] > $feature["field2"], $feature["field1"], 0) iif($feature["field1"] > $feature["field2"], iif($feature["field2"] = 0, $feature["field3"], $feature["field4"]), 0) | Returns field1 if field1 is greater than field2, and 0 otherwise. Returns the result of the second iif function if field1 is greater than field2, and 0 otherwise. |
When | when(<expression1> , <result1> , <expression2> , <result2> , ... , <expressionN> , <resultN>, <default>) | Evaluates a series of expressions in order until one evaluates to true.
| when(($feature["field1"] + 10) > 1, 1,($feature["field2"] + 10) > 2 , 2, $feature["field3"]) | If field1 + 10 is greater than 1, it returns 1. If not, it checks if field2 + 10 is greater than 2. If yes, it returns 2. If not, it returns field3. |
Decode | decode(<conditional val> , <case1> , <result1>, <case2>, <result2>, ... <caseN>, <resultN>, <defaultValue> ) | Evaluates an expression and compares its value with subsequent parameters. If the expression matches, it returns the next parameter value. If none match, there is the option for the last parameter to be a default return value.
| decode($feature["field1"] + 3 , $feature["field1"], 1, $feature["field2"], 2, 0) | Compares equality between the conditional val field1 + 3 and case1 field1. If true, it returns 1. If false, it compares the equality between field1 + 3 and field2. If true, it returns 2; otherwise, it returns 0. |