Note:
This tool is now available in Map Viewer, the modern map-making tool in ArcGIS Online. To learn more, see Overlay Layers (Map Viewer).
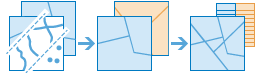
 The Overlay Layers tool combines two layers into a single layer using one of three methods: Intersect, Union, or Erase.
The Overlay Layers tool combines two layers into a single layer using one of three methods: Intersect, Union, or Erase.
Workflow diagram
Examples
The Half-Earth Project is working to conserve half the earth's land and sea in order to protect enough habitat for 85 percent or more of Earth's species. GIS analysts with the project use spatial analysis to determine which habitats should be protected based on their species diversity and rarity. Overlay Layers is used to clip the species data to a specific study area, such as countries in Africa.
See the Use species distribution patterns to assess protected areas lesson for the complete workflow.
The Loudoun County Board of Supervisors is searching for a suitable location for a new hospital. The site must be within two miles of urban areas, be more than a 20-minute drive from the current main hospital, and be within one mile of main roads. Buffers and drive times are used to create layers based on the stated criteria, and Overlay Layers is used to combine the layers to determine which areas meet all the criteria.
See the Site a new hospital lesson for the complete workflow.
Usage notes
The Overlay Layers tool requires two inputs: an input layer and an overlay layer. The availability of overlay method options depends on whether the input and overlay layers are points, lines, or areas.
When using the Erase overlay method, the input features must be of the same or lesser order feature type of the overlay layer. The following erase options are supported:
- A point feature can be erased by point, line, or area features.
- A line feature can be erased by line or area features.
- An area feature can be erased by area features.
| Overlay method | Input features | Overlay features | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Points, lines, or areas | Points, lines, or areas | The features or portions of features in the input that are overlapped with the overlay features are kept. You can specify the type of output as Points, Lines, or Areas when intersecting line or area features. The dimension of the output geometry type must be the same or less than both the input and overlay dimensions, where Points=0 dimensions, Lines=1 dimension, and Areas=2 dimensions. This is the default method. |
| Areas | Areas | The input and overlay areas are combined. |
| Points | Points, lines, or areas | The features or portions of features in the input layer that do not overlap with the areas in the overlay layer. |
Lines | Lines or areas | ||
Areas | Areas |
The type of result features will depend on the overlay method and inputs. All of the attributes from the input and overlay layer will be carried over to the result layer.
If Use current map extent is checked, only the features in the input and overlay layer that are visible within the current map extent will be overlaid. If unchecked, all features in both the input layer and the overlay layer will be overlaid, even if they are outside the current map extent.
Tip:
Click Show Credits before you run your analysis to check how many credits will be consumed.
Similar tools
Use Overlay Layers to combine two layers into a single layer using an Intersect, Union, or Erase method. Other tools may be useful in solving similar but slightly different problems.
Map Viewer Classic analysis tools
If you are combining features of the same type into a single feature layer regardless of the spatial relationship, use the Merge Layers tool.
ArcGIS Pro analysis tools
Overlay Layers performs the function of the Intersect, Union, and Erase tools.


