 Available in big data analytics.
Available in big data analytics.
The Aggregate Points tool
 collects and summarizes point features within area features. The boundaries from the area features are used to collect the points within each area; they are then used to calculate statistics. The resulting layer contains the count of points within each area as well as summary calculations.
collects and summarizes point features within area features. The boundaries from the area features are used to collect the points within each area; they are then used to calculate statistics. The resulting layer contains the count of points within each area as well as summary calculations.
Workflow diagram
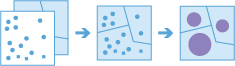
Example
The following is an example use case for the tool:
Tornadoes are a violent type of storm that occurs in the United States. You want to know the effect of tornadoes, including loss of life, injuries, property damage, and financial loss, in each state and county. You have access to tornado locations, but you need a better way to visualize the data within certain areas. You can aggregate the tornado data into state and county boundaries and normalize the data by population to find the areas most affected by tornadoes.
Usage notes
Keep the following in mind when working with the tool:
- The output layer is always a polygon layer. Only the polygon bins or features where points occur are returned.
- You can provide the area layer for the analysis, or generate bins of a specified size and shape (hexagon or
square) to aggregate point features. The bin size
specifies how large the bins are. If you are aggregating into
hexagons, the size is the height of each hexagon and the width of
the resulting hexagon is two times the height divided by the
square root of three. If you are aggregating into squares, the bin size
is the height of the square, which is equal to the width.

- If time is enabled on the target data, you can apply time steps to the analysis.
- The most basic aggregations calculate the number of points in each area. Statistics—including Count, Sum, Min, Max, Range, Mean, and Standard Deviation—can be calculated on numerical fields, and statistics, such as Count and Any, can be calculated on string fields. The statistics are calculated in each area separately.
The following are example return values:
- When Count is applied to a field, it returns a count of the nonnull values present in the field.
- When Any is applied to a string field, it returns a single string present in the field.
- The Aggregate Points tool allows you to analyze using time steps. Each time step is analyzed independently of features outside of the time step. To use time steps, the target data must be time enabled and represent an instant in time. When time steps are used, output features are time intervals represented by the StartTime and EndTime fields.
- If you specify the time step Interval, Repeat, or Alignment option and time is not enabled on the data, an error occurs when the tool is run.
- The time step options can be a date and time value or a date-only value; it cannot be a time-only value.
- The Aggregate Points tool requires that the target data is projected or that the target data is set to a projected coordinate system. If the target data is not in a projected coordinate system and you do not set one, the tool automatically applies the World Cylindrical Equal Area projected coordinate system to the data you are analyzing.
Parameters
The following are the parameters for the tool:
| Parameter | Description | Data type |
|---|---|---|
Target data | The point features that are aggregated into bins or polygons. | Features |
Join data (optional) | The polygon features the target data is aggregated with. A join data source is required to aggregate data into polygons. | Features |
Aggregate points into | Specifies how the target data will be aggregated. The options are the following
| String |
Bin type (optional) | The bin shape that will be used to create the bins. Options are Square (the default) and Hexagon. If a source is connected to the join port, this parameter is not available. Note:This parameter is only available if the Aggregate points into (Polygon or Bin) parameter is set to Bins. | String |
Bin size (optional) | The distance interval that represents the bin size into which the target data will be aggregated. For square bins, the bin size represents the height of a square. For hexagon bins, the bin size represents the height between two parallel sides. If a source is connected to the join port, this parameter is not available. Note:This parameter is only available if the Aggregate points into (Polygon or Bin) parameter is set to Bins. | String |
Interval (optional) | The duration of the time step. Use this option only if the target data is time enabled and represents an instance in time. | String |
Repeat (optional) | Specifies how often the time-step interval occurs. Use this option only if the target data is time enabled and represents an instance in time. | String |
Alignment (optional) | The reference time with which to align the time steps. The default is January 1, 1970, at 12:00 a.m. Check this parameter's check box to choose a date and time range. Use this option only if the target data is time enabled and represents an instance in time. | Int64 |
Summary fields (optional) | The statistics that will be calculated for specified fields. Different statistics are available depending on whether the specified field is a string, numeric, or date field.
| String |
Output layer
The output layer contains all original fields from the area features and the COUNT field. The COUNT field represents the number of point features from the target data aggregated into this polygon feature. The data type of the COUNT field is Float64. If you configure summary fields, those fields are also calculated for the output layer.
Consideration and limitation
Lines and polygons cannot be aggregated within boundaries using the Aggregate Points tool.