Python code can be executed either in the interactive Python console or from the Python Editor.
Python Console
The Python Console has two modes:
- Interactive mode to directly execute Python code.
- Output mode to display print and error messages of a running script.
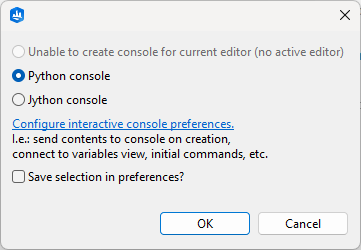
To get an interactive Python Console, open a Console view (Window > Show Console), and select Python Console from the drop-down list below the small triangle in the toolbar.

By default, you will be asked to choose the desired interpreter. Alternatively, you can configure a default Console interpreter in the Preferences at Edit > Preferences > Python > Interactive Console > Default interpreter.
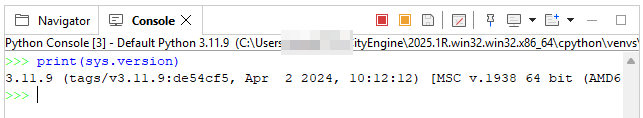
You can open multiple console views at once ("New Console View" in the console drop-down menu) and assign them different consoles. It is for example handy to have a script output console and an interactive console side-by-side.
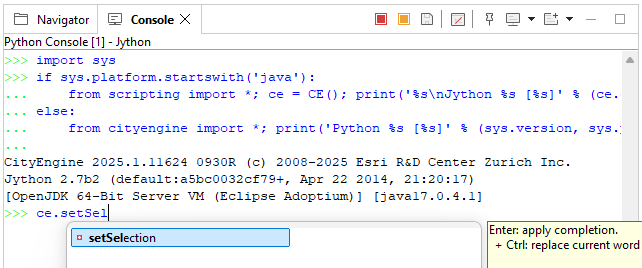
In the interactive console, the specific CityEngine API commands as well as conventional Python commands can be typed. To execute a command line, press Enter. Use Ctrl+Space to show the command completion popup, which displays possible commands depending on your typing. The last used command can be called by pressing the Up Arrow key.
See Commands by Category or Command Reference for a list of available CityEngine functions.
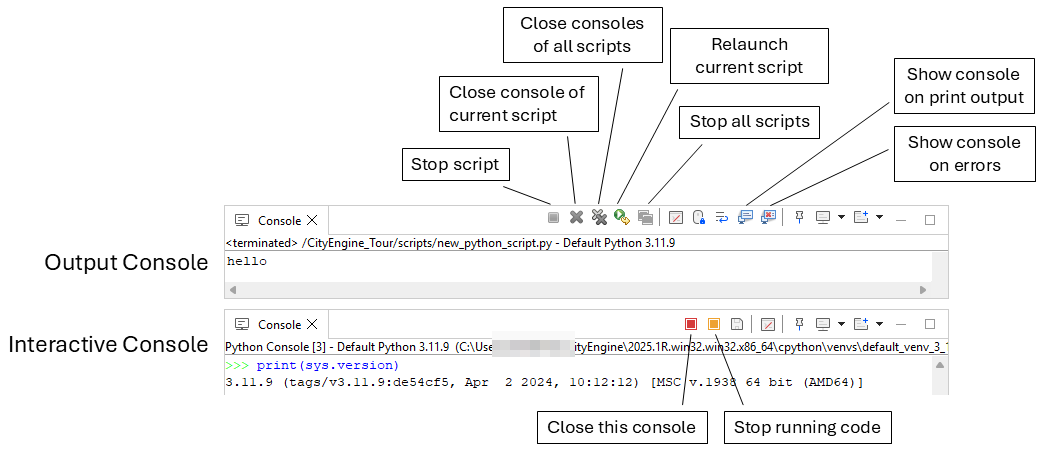
Console Script Execution Controls
The console toolbar has a number of script execution control buttons to stop and relaunch scripts as well as close consoles.
Python Editor
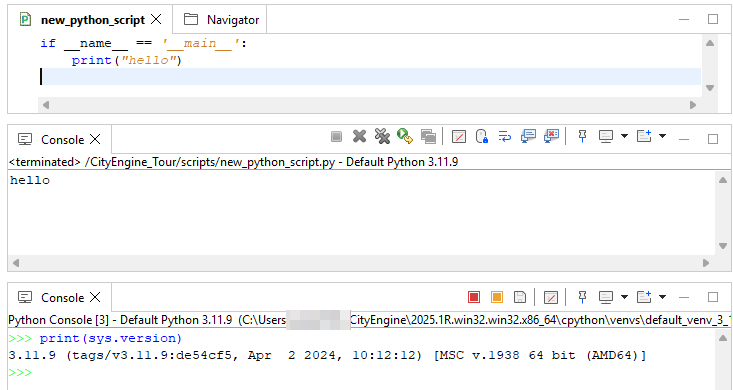
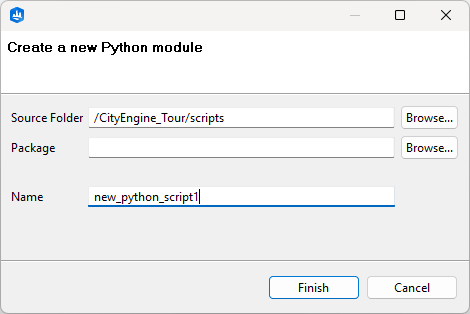
The Python Editor offers a more convenient way to edit and execute scripts. Create new script modules via File > New > Python Module. Select the scripts folder of your current project as Source Folder, and specify a Name for your module.
Four module templates are available:
<Empty> | Creates an empty template |
Module: Class | Creates an empty python class |
Module: Export | Creates callback calls to be used with the Python-based exporter |
Module: Main | Creates an executable script |
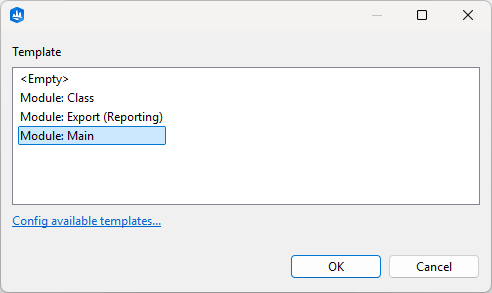
Choose the scripts folder of a CityEngine project as Source Folder, set a Name for the module and choose one of the templates.
New modules created via this dialog contain the following lines.
import sys
if sys.platform.startswith('java'):
from scripting import *
else:
from cityengine import *
# get a CityEngine instance
ce = CE()
- An import statement that imports the API-specific scripting (Jython) or cityengine (Python 3) module.
- From this module, the main instance ce is created, which allows to calling all CityEngine Python commands
Running a script
To execute a script in the Editor, select Python > Run Script in the menu or press F9. (Focus needs to be on a Python script in the editor area to enable the Python menu).
Cancel all running Python scripts by choosing Terminate from the Output Console toolbar (or by pressing Ctrl+Alt+C). If the Output Console is not visible, use Window > Show Console to open a Console view.
As in the interactive Console, you can use Ctrl+Space to trigger the command completion.
Below you see the Main template extended with the "export" function. This script exports selected models as .obj files into the model folder of the current project:
import sys
if sys.platform.startswith('java'):
from scripting import *
else:
from cityengine import *
# get a CityEngine instance
ce = CE()
def export(objects):
dir = ce.toFSPath("models/")
name = "pythonTriggeredExport"
settings = OBJExportModelSettings()
settings.setBaseName(name)
settings.setOutputPath(dir)
ce.export(objects, settings)
if __name__ == '__main__':
export(ce.selection())
Importing modules
By default, a script will see all modules in the "scripts" folder of the current project as well as any builtin modules (builtin modules differ between Jython 2.7 and Python 3).
>>> import random
>>> random.randint(0,100)
42
To import custom modules/scripts, their parent folder needs to be part of the "python path". There are two ways to modify the "python path":
- In code, by editing the `sys.path`, for example:
import sys sys.path.append("... path to module X ...") import X - In UI, by adding paths (e.g. the "scripts" folder of another project) in the project properties under "External Libraries":

Scripts shortcut menu
To quickly start a Python script it can be placed in the scripts menu Scripts > Add scripts.
See also