Work with proxies
In this topic
- Specify CORS-enabled servers (optional)
- Configure the internal proxy
- Test the proxy
- Configure an optional upstream proxy
Under some circumstances, Esri Maps for SAP BusinessObjects uses an internal proxy mechanism to broker communication with the ArcGIS platform (in addition to any web services referenced by retrieved ArcGIS items). When required, Esri Maps for SAP BusinessObjects sends HTTP requests to the proxy, and the proxy forwards the requests to the remote web server (such as ArcGIS). The proxy then relays the response back to Esri Maps for SAP BusinessObjects.
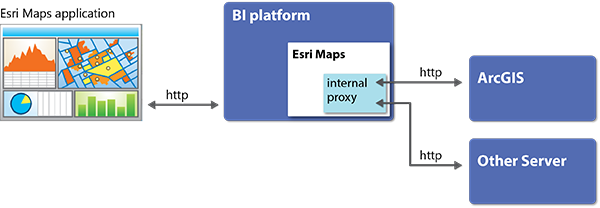
The internal proxy is not used if Esri Maps for SAP BusinessObjects and all the data and web services it uses are on the same domain, or if both the client browser and all servers support Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS). In most production environments, however, this configuration is not common, and configuring the internal proxy is recommended.
Specify CORS-enabled servers (optional)
Most modern browsers use the recommended standard, Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS). The CORS standard adds headers to the HTTP specification that allow servers to describe the set of origins that are permitted to read resources and services using a web browser.
Esri Maps for SAP BusinessObjects automatically detects servers that use Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS) and communicates with these servers without issue. In some cases, however, the initial request (an HTTP POST, for example) is automatically routed through the Esri Maps for SAP BusinessObjects internal proxy, even though the server is CORS-enabled. As an Esri Maps for SAP BusinessObjects administrator, you can list the URLs for known CORS-enabled servers in the Esri Maps for SAP BusinessObjects configuration file (settings.js) to ensure that all calls originating from those locations are automatically considered CORS-enabled, thereby bypassing the proxy.
Note:
Servers listed in the corsEnabledServers property must be preconfigured to support CORS. Before adding a server URL to this list, verify that the server is, in fact, CORS-enabled. If a server specified in this setting is not CORS-enabled, communication with the Esri Maps for SAP BusinessObjects server will fail. For more information, see Enable Cross-Origin Resource Sharing
To specify CORS-enabled servers:
- Use a standard text editor to open the application's configuration file.
The configuration file is in the following location: <Tomcat installation directory>\webapps\em4bobj\em4bobj\dashb\configuration\settings.js
- In the corsEnabledServers property, specify the URLs of the servers to be automatically considered CORS-enabled.
Each URL must be enclosed within quotation marks, with multiple URLs separated by commas.
For example: corsEnabledServers: ["mapserver.mycompany.com", "otherserver.othercompany.com"]
Note:
You cannot include an instance of Portal for ArcGIS that uses web tier authentication in this list. In such an instance, however, automatic detection of CORS will always occur without involving the proxy.
- Save and close the settings.js file.
- Restart your web application server. Clearing the browser cache may be required to implement changes.
Configure the internal proxy
Although the internal proxy is designed to work with minimal custom configuration, you can customize its settings to allow only requests to specific servers; that is, you can specify the resources to which the proxy will forward requests.
To configure the internal proxy settings, modify the proxy configuration file using a standard text editor.
The proxy configuration file (proxy.config) is located at <Tomcat installation directory>\webapps\em4bobj\em4bobj\dashb\proxy.config.
Note:
After you save the proxy configuration file, restart your web application server. It may be necessary to clear the browser cache to activate changes to the proxy file.
To define the URLs that Esri Maps for SAP BusinessObjects is allowed to access, specify each individual URL in a separate serverUrl child element. Create a separate serverUrl element for every server that Esri Maps for SAP BusinessObjects must access to retrieve map services.
Note:
Setting the serverUrls element's mustMatch attribute to true specifies that the proxy can access only the servers explicitly listed. Setting this attribute to false means that the proxy can access any server, and ignores any server listed as a serverUrl.
For example:
<ProxyConfig>
<serverUrls mustMatch="true">
<serverUrl url="http://www.arcgis.com"/>
<serverUrl url=”http://geoenrich.arcgis.com”/>
<serverUrl url=”http://geocode.arcgis.com”/>
<serverUrl url=”http://gis.mycompany.com/arcgis/rest/services”/>
</serverUrls>Test the proxy
To test the internal proxy, route an HTTP request through it. If the proxy returns the expected value, it is working correctly. The following steps provide examples of calls that simulate the HTTP traffic that Esri Maps for SAP BusinessObjects would generate.
- To verify the location of the Esri Maps for SAP BusinessObjects internal proxy, type its URL in a web browser's address bar.
http://<mySAPBIPlatformWebServer>/em4bobj/em4bobj/dashb/proxy.jsp
When you successfully access the internal proxy, the page displays a time stamp, for example, Thu Oct 02 07:34:52 PDT 2014. If you do not receive the expected response, verify your internal proxy configuration settings.
- Verify that you can connect to a known resource.
For example, each of the following URLs should return a JSON object that describes the version of the software installed on the server.
- ArcGIS Online: http://www.arcgis.com/sharing?f=pjson
- Portal for ArcGIS instance: http://myPortal/gis/sharing/?f=pjson
- Route traffic through the internal proxy.
For example, each of the following URLs should return a JSON object that describes the version of the software installed on the server:
- ArcGIS Online: http://<mySAPBIPlatformWebServer>/em4bobj/em4bobj/dashb/proxy.jsp?http://www.arcgis.com/sharing?f=pjson
- Portal for ArcGIS instance: http://<mySAPBIPlatformWebServer>/em4bobj/em4bobj/dashb/proxy.jsp?http://myPortal/gis/sharing/?f=pjson
Note:
If routing a call to the internal proxy does not return the expected result, you may need to use an upstream proxy to access the resources. In this case, configure the upstream proxy, and then run the tests in this section again. The internal proxy will route traffic through the upstream proxy and return the expected result to the web browser. For more information, see Configure an optional upstream proxy.
A successful result means that your proxies are properly configured and working as expected.
Configure an optional upstream proxy
In situations in which Esri Maps for SAP BusinessObjects must use its internal proxy, the internal proxy must be able to forward HTTP requests to the intended target resources (such as map services). In some environments, firewall rules prevent these requests from being sent; for example, the firewall may prevent HTTP traffic from leaving the internal network.
To solve this problem, you can configure an upstream forwarding proxy.
An upstream proxy allows connections outside the network without compromising the security of the internal network. One common approach to using an upstream proxy is to place a proxy server in a perimeter network to protect the internal network.
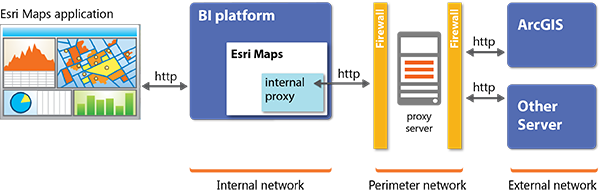
The upstream proxy itself represents an enterprise-level, third-party (non-Esri) solution. It is not part of Esri Maps for SAP BusinessObjects.
Note:
Esri Maps for SAP BusinessObjects does not support upstream proxy servers that require authentication.
The Esri Maps for SAP BusinessObjects proxy configuration file contains elements that allow you to configure an upstream proxy.
To configure upstream proxy settings, modify the proxy configuration file using a standard text editor.
- Set the useUpstreamProxy element's enabled attribute to true.
- Specify the URL of the upstream proxy server using the following convention:
http://<address>:<port>where:
- address—The address of the proxy server, for example, proxy.mycompany.com
- port—The port number assigned to the proxy server, for example, 8888
For example:
<useUpstreamProxy enabled = true> http://proxy.mycompany.com:8888 </useUpstreamProxy>Note:
If you use an IP address to specify the location of your proxy server, do not type leading zeroes; for example, use 130.25.0.1 instead of 130.025.000.001.
If you do not know the web address or port number of your proxy server, contact your network administrator.
- To test the upstream proxy, route a request through the internal proxy, which will in turn route the call through the upstream proxy. For more information, see Test the proxy.