ArcGIS Velocity allows you to explore dynamic aggregation visualizations and save visualization and symbology settings for map image layers. These visualizations are useful to control dynamic aggregation visualization settings in map image layers to effectively visualize large volumes of data.
Data stored by Velocity is backed by a spatiotemporal big data store where data is indexed and aggregations are available.
For example, consider an analytic that creates an output layer using the Feature Layer (new) output and captures vehicle location observations from connected cars. The resulting feature layer would likely contain millions of records over time. Rendering millions of feature points is not an effective visualization strategy for a web map. Instead, you can use the map image layer that is created with every feature layer generated by Velocity. These map image layers allow dynamic aggregation visualization options to render geohash, square, hexagon, or triangle bins representing a count of features in each bin. You can symbolize each bin with a summary statistic on an attribute field of the data to represent the nature of features in each bin.
Using the map image layer editing interface, you can explore aggregation and statistic settings, bin styles, feature styles, and label styles. Once you are satisfied with the settings, you can save them so that any user who uses the map image layer can visualize the selected dynamic aggregation visualization.
Edit map image layer
Complete the following steps to edit a rendering of a map image layer:
- In the Velocity app, click Layers from the main menu.
- Locate the map image layer in the list and click Edit.
- Click one of the following tabs to edit the map image layer:
- Aggregation settings
- Bins
- Feature settings
- Labels
Aggregation settings
The parameters in the Aggregation settings pane control the general settings for feature aggregation, specifically what is represented by the aggregation (raw feature count or a feature statistic), the style of aggregation, the feature threshold, and bin size.
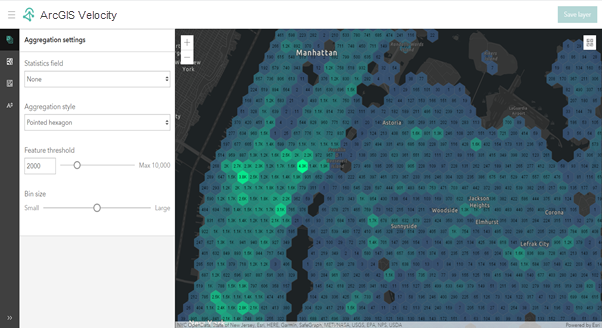
The parameters for the Aggregation settings pane are described below:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Statistics field | Specifies the field to use for statistic calculation. If None is selected, the feature aggregation value represents a count of features in each bin. If a statistics field is selected, the Statistics type parameter value is applied to the values of the statistic field for features that fall within multiple bins. The feature aggregation bin is then styled according to the resulting value. For example, if the Statistic field value is Vehicle_Speed, and the Statistic type value is Average, each dynamic feature aggregation bin shows the average speed of all the vehicle observations in that bin. |
| Statistics type | Specifies the statistic type to apply to values in the selected statistic field. This parameter is only available if a statistics field is selected. The following statistics are available for the specified field data types:
|
| Aggregation style | Specifies the desired aggregation style. This represents the bin shape of the dynamic aggregation. The following options are available:
Note:Only aggregation styles specified when configuring the Feature Layer (new) output in the analytic are available on the drop-down menu. |
| Feature threshold | Specifies when the rendering style of the map service is switched between aggregation and discrete features. The default is 2000. When the number of features in the current map extent is more than the feature threshold specified, the layer is rendered using an aggregation style; if equal or less, the layer is rendered showing raw features. If set to 0, the layer always renders using aggregation. |
| Bin size | Specifies the size of the bins. The following options are available:
|
Bin styles
The parameters in the Bins pane control the style options for the fill style, outline style, and outline width for each dynamic aggregation bin. These parameters use the bin value as a weight to interpolate from the minimum to the maximum of the range values specified.
- A bin with a bin value equal to the minimum of the range value uses the minimum of the fill style, outline style, and outline width specified. A bin with the bin value equal to the maximum of the range value uses the maximum of the fill style, outline style, and outline width specified.
- If a bin value falls between the minimum and the maximum range value, the aggregation renderer uses its bin value as a weight to interpolate from the minimum to the maximum of range values to determine the fill style, outline style, and outline width for the bin.
- If a bin value falls outside of the range values, the aggregation renderer uses the minimum value if its bin value is smaller than the minimum range value and use the maximum value if its bin value is greater than the maximum range value.
- If you leave the minimum and maximum range values blank, the aggregation renderer calculates the minimum and maximum bin values from the current map extent and use them as the minimum and maximum for the range values.
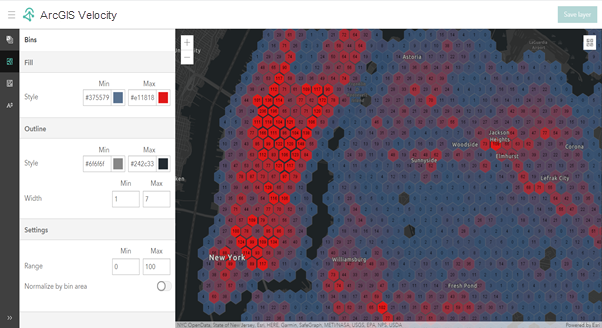
The parameters for the Bins pane are described below:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Fill color | The minimum and maximum fill colors. If a bin value falls between the minimum and the maximum range value, the aggregation renderer uses its bin value as a weight to interpolate from the minimum to the maximum of range values to determine the fill style for the bin. |
| Outline color | The minimum and maximum outline colors. If a bin value falls between the minimum and the maximum range value, the aggregation renderer uses its bin value as a weight to interpolate from the minimum to the maximum of range values to determine the outline style for the bin. |
| Outline width | The minimum and maximum outline width. If a bin value falls between the minimum and the maximum range value, the aggregation renderer uses its bin value as a weight to interpolate from the minimum to the maximum of range values to determine the outline width for the bin. |
| Range | The range of values to which varying fill styles, outline styles, and outline widths apply. Turning on the Enable custom range option allows you to set the maximum and minimum range values. If a bin value falls outside of the range values, the aggregation renderer uses the minimum value if its bin value is smaller than the minimum range value and use the maximum value if its bin value is greater than the maximum range value. If you leave the minimum and maximum range values blank, the aggregation renderer calculates the minimum and maximum bin values from the current map extent and use them as the minimum and maximum for the range values. |
| Settings | Bins that appear the same size on a map can cover a different geographically sized area. For example, a bin at the equator covers a larger geographic area than a bin at the north pole even if the two bins are the same size in a map. If their bin values are the same, the bin at the equator has less density compared with the bin at the north pole. When the Normalize by bin area option is turned on, the rendering is normalized. For example, for two bins with the same value, the bin at the equator has a lighter color and the bin at the north pole has a darker color, assuming the fill color the maximum value uses is a darker color than the minimum value. When the Normalize by bin area option is turned off, all bins are treated as the same-sized geographic area. |
Feature settings
The parameters in the Feature Settings pane control how raw features are rendered. Individual features are only rendered when the number of features to be rendered in the current map extent is less than the feature threshold specified. The raw feature rendering of the map image layer is limited to simple vector symbols (circles, squares, diamonds, pointers, and so on). Raw features can be rendered using the Simple, Class breaks, or Unique value renderer option.
Simple
Raw features can be rendered using the Simple renderer option. The simple renderer renders all features in a feature layer with one symbol.
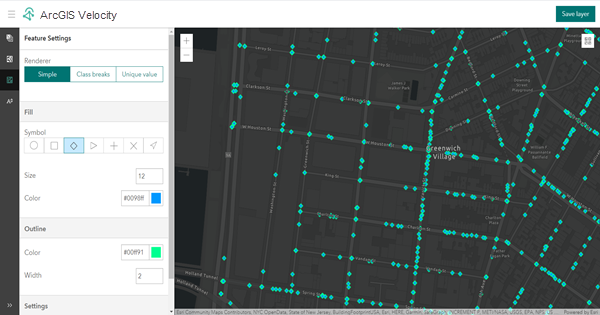
The parameters for the Simple renderer option are described below:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Fill | Specifies the color for each feature. The Color option allows you to choose a feature color using a color picker or by entering a hexadecimal color code. |
| Outline | Specifies the border surrounding each feature. The Width and Color options allow you to set the thickness and color of the feature's outline. |
Class breaks
Raw features can be rendered using the Class Breaks renderer option. The class breaks renderer defines the symbol for each feature in a feature layer based on the value of a numeric attribute. The numeric attribute values are used to define data ranges for the classes. Each feature is assigned a symbol based on the class break of its numeric attribute value.
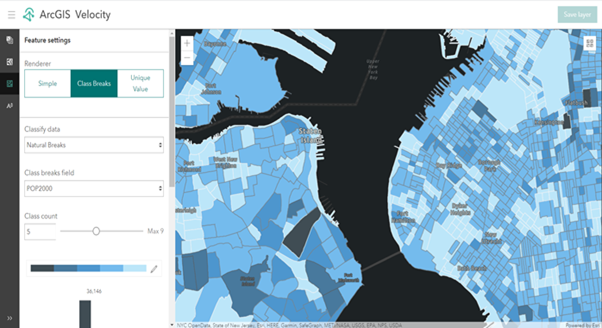
The parameters for the Class Breaks renderer option are described below:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Classify data | Specifies the classification method. Options are manual breaks, natural breaks, equal interval, standard deviation, and quartile. |
| Class breaks field | Specifies the field used for calculating class break values. |
| Class count | The total number of classes. The classes can be manually adjusted in the class breaks histogram. |
| Color ramp | Applies a range of colors to the classes. Choose one of the color ramps or apply a unique color ramp using the fill style of your bins. |
| Outline | Specifies the border surrounding each feature. The Width and Color options allow you to set the thickness and color of the feature's outline. |
Unique value
Raw features can be rendered using the Unique Value renderer option. The unique value renderer renders all features in a feature layer based on one or more matching attributes.

The parameters for the Unique Value renderer option are described below:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Unique value field | Specifies the field used for determining unique values. |
| Manage Values | Defines the unique value to symbolize. Values that are not present in the current data set can be manually added. |
| Color ramp | Applies a range of colors to the unique values. |
| Outline | Specifies the border surrounding each feature. The Width and Color options allow you to set the thickness and color of the feature's outline. |
Labels
The parameters in the Labels pane control how aggregation bins are labeled.

The parameters for the Labels pane are described below:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Show labels | Specifies whether labels are shown on aggregation bins. |
| Font | The font to be used for labels. The following options are available:
|
| Size | The size of the labels. |
| Color | The color of the labels. |
| Style | The style of the labels. The following options are available:
|
| Format | The format to use for labels. This is a text value format pattern based on the Java decimal format specification. For more information, refer to the label format parameter examples. |
The label format parameter examples are described below:
| Raw value | Label format pattern | Resulting label | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
123456.789 | ###,###.### | 123,456.789 | The pound signs (#) denote digits, the comma is a placeholder for the grouping separator, and the period is a placeholder for the decimal separator. |
123456.789 | ###.## | 123456.79 | The value has three digits after the decimal point, but the pattern has only two. The format method handles this by rounding up. |
123.78 | 000000.000 | 000123.780 | The pattern specifies leading and trailing zeros, because the 0 character is used instead of the pound sign (#). |
12345.67 | $###,###.### | $12,345.67 | The first character in the pattern is the dollar sign ($). It immediately precedes the digit in the formatted resulting label. |
789,123,456,789 | ###.##KMB | 789.12B | The KMB characters indicate to represent billions with a B and round to the digits specified by the pound signs (#). |
789,123,456 | ###.#kMG or ###.##KMB | 789.1M | The kMG or KMB characters indicate to represent millions with an M and round to the digits specified by the pound signs (#). |
Save changes
Optionally, you can save the settings and changes you have made. When you click the Save option, client apps, such as ArcGIS Online web maps that use the map image layer, are symbolized and rendered according to the dynamic aggregation and feature rendering settings.
For example, the image below shows a web map in which aggregation and label settings were modified.
