Building information modeling (BIM) is a holistic process for creating and managing information for a construction project across multiple disciplines. Examples for the use of multi-disciplinary models are buildings, roadways, railroads, and bridges. You can integrate, visualize, analyze and maintain your digital models in ArcGIS. ArcGIS supports digital model files from Industry Foundation Classes (IFC) and Autodesk Revit (RVT). To integrate digital models (IFC or Revit) models into your GIS system you have the following workflows available.
Workflows
ArcGIS supports several workflows to integrate BIM files in GIS. For example, you can work with a IFC or RVT file directly in ArcGIS Pro and create a building layer. Or you can share a building scene layer to make the layer accessible across your organization. In both cases the structure of the digital model is translated into a schematic structure that best represents the building, for example.
Inspect your BIM models
The most common workflow to bring BIM models to ArcGIS is via ArcGIS Pro. To make BIM files accessible in your organization you need to inspect them as a first step. The following checklist will help you to understand your digital model better.
| Questions | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|
Does the 3D model draw at the correct location? | ||
Are you working with Revit and the file requires an upgrade? |
If you answer any of the questions in the checklist with yes you will have to make changes to the BIM file directly in ArcGIS.
Does the 3D model draw at the correct location?
Any geospatial data require a spatial reference to locate the data at the correct x, y and z coordinate. When you bring data from other systems into ArcGIS the information about the spatial reference or the coordinates can be missing or relative to a project location. For example, if you load a BIM file it might be drawing in the Atlantic Ocean close to Africa. This is a clear indication that your data is missing spatial reference. You will need to georeferenced the data first. The best practice is use the validate position page (VPP) workflow Geolocating a Digital Model.
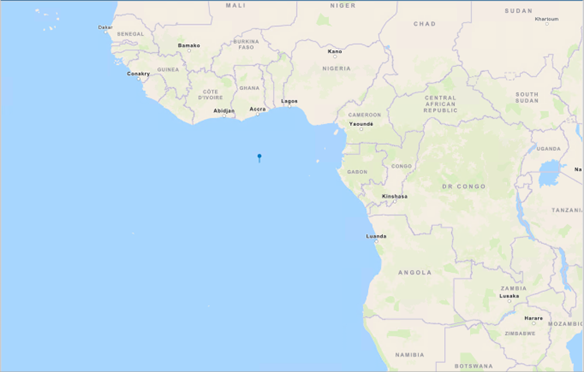
In case your model draws exactly at the position you expected it to be. The answer to the question is yes and no further action is required.
Are you working with Revit and the file requires an upgrade?
ArcGIS supports IFC and Revit as BIM files. Both formats continue to evolve, and newer versions might contain additional information you want to also view in ArcGIS. In the case of Revit you can upgrade the Revit file version in ArcGIS Pro. The upgrade of the Revit file will help ArcGIS Pro to read and load the data faster. If you are going to upgrade the Revit file, please make a copy first and upgrade the copy. This assures that you can continue working with your original Revit file in your modelling software.
If you are working with IFC no further action is required.
Load a 3D digital models (IFC or Revit) files in ArcGIS Pro
To get a deeper understanding of your model you need to first find out how it will be visualized and what attributes will be accessible in ArcGIS. You can drag and drop the BIM file in a local or global scene in ArcGIS. The model will be added as a building layer. The following checklist will help you to understand your digital model better.
| Questions | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|
Does the exterior shell of the building layer show all details you need as overview? | ||
Do you need to adjust the BIM model to show the correct features and categories? | ||
Do you have multiple models representing the same single building or structure? | ||
Are you planning to edit the BIM model in ArcGIS or continue working in your modeling software? |
If you answer any of the questions in the checklist with yes you will have to make changes to the BIM model in your modeling software or directly in ArcGIS.
Does the exterior shell of the building layer show all details you need as overview?
The exterior shell of the building layer shows an overview of the digital model with exterior element and without interior details. The overview gives you a visual representation of all structures while the disciplines contain all sublayers for architectural, structural, piping and others. When view the BIM model on the web you usually first see the exterior shell. It is important that the exterior shell contain all the elements you want to have visible. When you load the BIM file for the first time in ArcGIS Pro, you can turn all layers off except the ExteriorShell layer. You can compare the building layer with all disciplines turned on with only the ExteriorShell layer to evaluate if all details are present. If not, enough details are visible, you will have to make changes to the digital model.
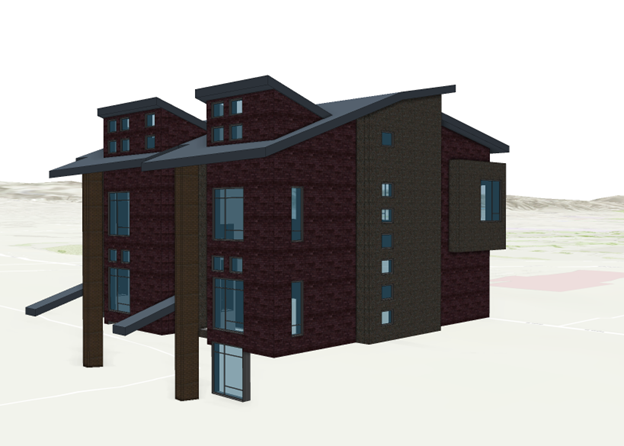
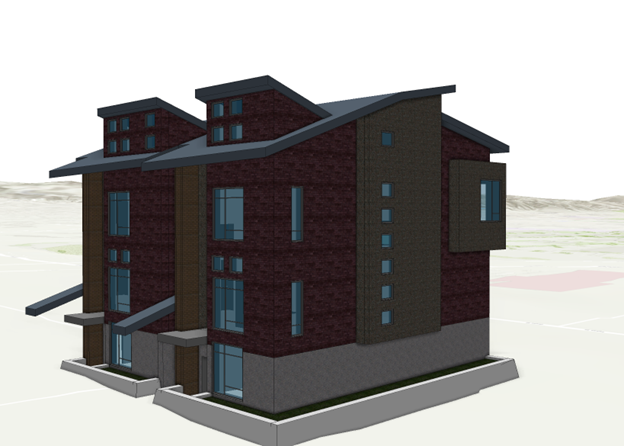

In the example above you notice that some walls are missing in the exterior shell. To add missing features, you have the following options:
- Export the digital model to a GDB and then copy and paste the features from the detailed category layer into the exterior shell layer.
- Run the geoprocessing tool append to add missing elements from the exterior shell based on a selection query.
- Set the attribute Function = Exterior in the digital model. This step is recommended if you are adding the BIM model as read only to ArcGIS and continue to work in other modeling software to maintain the BIM file.
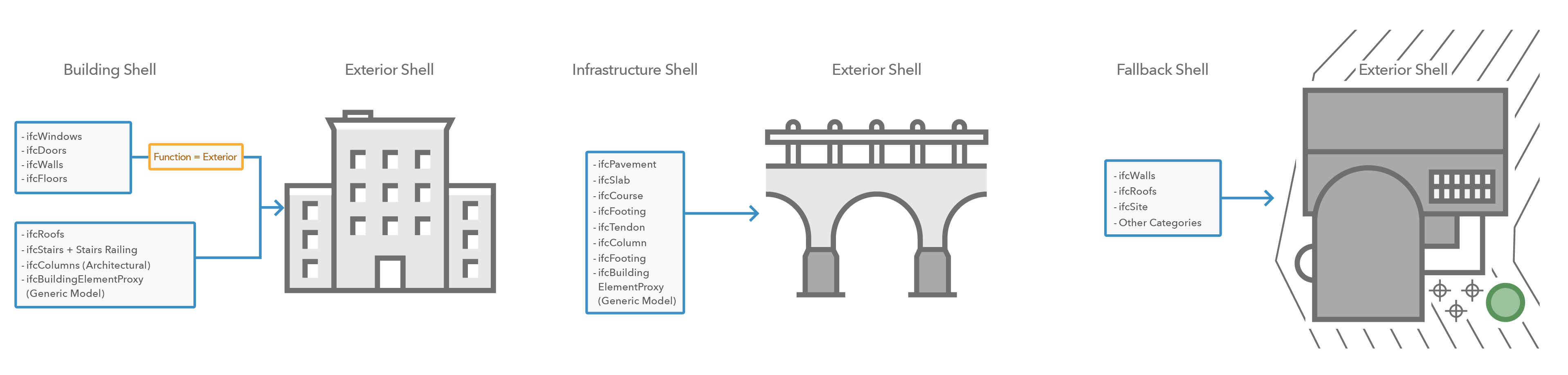
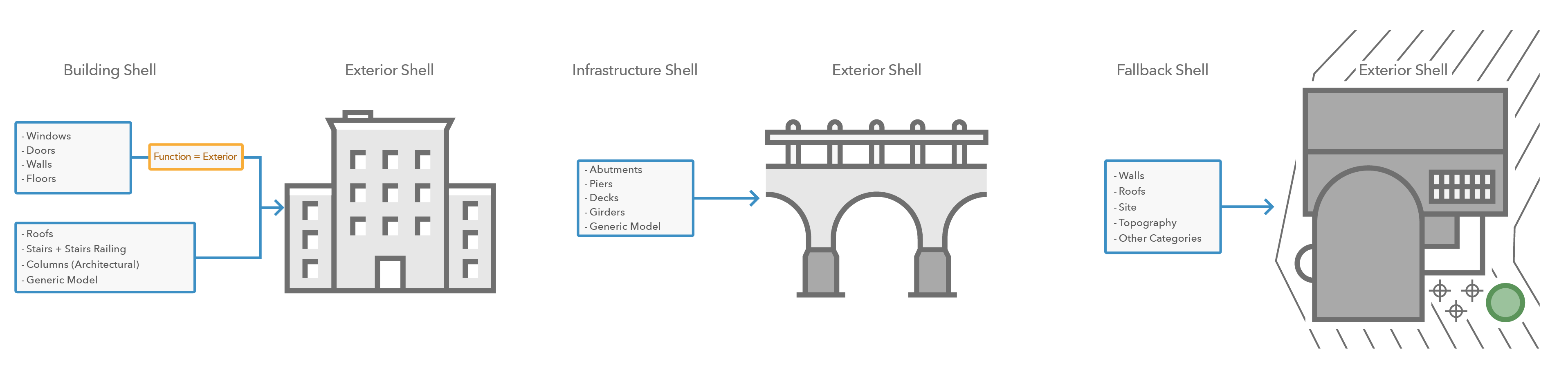
Do you have multiple models representing the same single structure?
In construction projects it is common that every discipline works independently on their BIM file and that you receive multi-disciplinary digital models for the same building or structure. In ArcGIS you want to view all the digital models belonging to the same building or structure as one layer. For example, you might have to combine different disciplines like architecture and piping. In some cases you might have different files for each building, but you would like to consider a group of buildings as one digital model.
If you do have multiple models and want to merge them you will need to run a geoprocessing tool BIM File To Geodatabase. Your BIM file will be converted in a geodatabase including all categories. Consider this step if you plan to build a digital twin for example, where all features, attributes, and experiences will be maintained in ArcGIS.
After the BIM file has been converted into a geodatabase you can run the Make Building Layer to create a building layer from the new data source.
Are all elements assigned to the correct category?
Depending on how the multi-disciplinary model is organized it might be more straightforward to represent the disciplines and categories in the defined schema for ArcGIS. For example, you might notice after you added the digital model to ArcGIS Pro that some of the elements are in the wrong category, like pipes being categorized as generic model. To move features into the correct category you can:
- Use the geoprocessing tool Split By Attributes. The generic feature class will be split by a key attribute that allows you to reorganize the data. Doing this will require some exploration and understanding of the data.
- Change the attributes in the digital model by using your modeling software.
Are you planning to edit the BIM model in ArcGIS or continue working in your modeling software?
Depending on the stage of the life cycle of your project you will have to decide on the storage of the multi-disciplinary model. If you are in the operational & maintenance (O&M) phase the building or structure is completed and the final version of the digital model has been saved. Often workflows like space management, asset management, and query information about specific elements are performed. It is best practice to convert the multi-disciplinary model to a geodatabase, since it will be the system of record. If your building is still in the construction phase y (30%, 60%., etc.) you can continue making all changes in the modeling software and import the BIM file as read only. You will still be able to view the digital model in the geospatial context of your city, for example.
Create a web layer
While you can work with BIM files directly in ArcGIS Pro you can also share the digital models as web layer across ArcGIS. This allows you to show a highly detailed multi-disciplinary models on the web and on mobile devices and make the details accessible to everyone with access to the web layer. You will need to clarify important questions for the loading and inspection of the BIM file, and you also must think about the consumption of the BIM file as web layer:
| Questions | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|
Do you plan to query features in the BIM model? | ||
Do you need preset filters in the BIM model? | ||
Do you plan to edit the BIM model? | ||
Will the BIM model be input to geoprocessing tools? | ||
Are you sharing the BIM model on the web? | ||
Do you have special requirements for pop-ups? | ||
Do you have restrictions for credit use? | ||
Do you need to connect the BIM model to other systems? |
If you have any questions answered with yes you will need to consider the following workflows.
Author a building scene layer
To view large amount of 3D data across ArcGIS you will need to create a building scene layer. In the case of digital models (Revit or IFC) a building scene layer is the recommended representation. In addition, you can create 3D object scene layer from individual category layers. However, you will lose the sematic context of the building if you review each category individually.
You can create a building scene layer as read only scene layer package (SLPK), ESLPK or i3sREST format. If you require editing, querying, and geoprocessing capabilities you will have to create a building scene layer with associated feature layer. Depending on the answer to the questions below you will have the following workflows.
Are you sharing the BIM file on the web?
One of the advantages of ArcGIS is that you can bring many different types of data together in a scene and view it in desktop, web, or mobile applications. In case you want to share the digital model with your audience over the web or on mobile devices you will have to create a building scene layer and share to ArcGIS Online or ArcGIS Enterprise.
You can cache the scene layer on your local machine or on the server. In case you cache on the server a scene layer with associated feature layer is created. The scene layer and associated feature layer build a unit combining the fast visualization of the scene layer with the edit, query, and geoprocessing capabilities of the feature layer. And if you cache on your local machine only visualization is available.
Do you have restrictions for credit use?
When you share your BIM file as building scene layer in ArcGIS Online you will be charged for the storage of the data. In case you require an associated feature layer in addition you will use credits for the feature layer.
If the digital model is edited, for example by changing the geometry or attributes, you will have to rebuild the scene layer cache. Since you are recreating the data additional credits will be used for rebuild of the cache. The same applies when you replace a read only layer.
While the creation and rebuild of the scene layer only creates costs for the data stored you will have to calculate additional costs for the associated feature layer. An associated feature layer will enable workflows like query, edit, connect to other systems, for example.
Do you plan to query features in the BIM file?
You can query a BIM file to find important information about a specific feature or a group of features. For example, you can create a query to find all fire safety doors in a building. You can query data by creating predefine queries using the Building Filter or by defining a query expressions for individual category layers. A building filter is a predefined query across all selected category layers. A query expression is dynamic that can be created or modified on the.
In case you don’t need to query the digital model you can create a read only building scene layer.
Do you plan to edit the BIM file?
A building or structure that has reached the operation and maintenance (O&M) phase can be managed in ArcGIS. If you need to edit the digital models geometry in ArcGIS you have the following options:
- Convert the BIM file to a Geodatabase using the BIM File to Geodatabase geoprocessing tool. The feature classes are editable in ArcGIS Pro.
- Share the building layer to ArcGIS online or ArcGIS Enterprise with the cache on server option. A scene layer with associated feature layer will be created and you have all options to edit the web layer in ArcGIS Pro.
In case the building is still in the design or construction phase and frequent updates are made to the digital model it is recommended to create a read only building scene layer as scene layer package (SLPK), Extracted scene layer package (ESLPK), or Indexed 3D scene layer REST (i3sREST) and replace the layer every time an update is available. You might only want to focus on the milestones you want to share with your audience within the digital twin and not each digital model that gets produced.
Will the BIM files be input to geoprocessing tools?
Geoprocessing is a framework and a set of tools to process geographic and related data. ArcGIS provides a large number of tools. If you plan to use geoprocessing extensively in your digital models you will have to:
- Convert the BIM file to a Geodatabase. When the category layers are converted to a feature class any tool accepting feature classes as input will work.
- Create a building scene layer with associated feature layer. Also, here the associated feature layer can be used in any geoprocessing tool that accepts the input type feature layer.
The project and clip tool will also work on scene layers with read only data sources. For example, your data might be in the local coordinate system of the construction site but you would like to show it in a web scene together with a 3D basemap and additional ancillary data. In this case you would project the building scene layer to the geographic coordinate system WGS1984 to be able to view the layer together with a global basemap.
Do you have special requirements for pop-ups?
When you click on a feature in your BIM model the attribute information will be displayed. In ArcGIS Pro you can configure which information will be shown and if you require additional information like diagrams, for example. The definition of pop-ups is an authoring step you can do for any type of building layer.
Do you need preset filters in the BIM file?
Building filters allow you to only view a subset of the building based on a query. For example, to display only aspects of a building required for safety and emergency you can filter the elements that belong to those categories. The safety inspection team can see where all the exit signs are located and or where all the fire extinguishers are located without having to find the details within your complex BIM model. In addition, you can subset the filter for safety and emergency by floors thus if multiple inspectors have to work together each inspector can access the data to the floor assigned to her. The use of filters is important if you plan to share your BIM models with a specific and or diverse audience that might not understand all the details of the building but need to review specific aspects of it.
Do you need to connect the BIM files to other systems?
In the operation and maintenance (O&M) phase of a building life cycle, you are often require to connect the GIS information to other systems. You can connect any tabular data to a feature layer in ArcGIS. After creating a relationship, you can publish the digital model as building scene layer and view the data from the digital model together with the related information in pop-ups for example. Or you can use the Esri software stack APIs to connect the feature layer to other systems.
Considerations
If you want to work with digital models in the operation and maintenance (O&M) phase of a buildings or structure life cycle it is best practice to convert the BIM file into a geodatabase representation so you can do any edits directly in ArcGIS. In case the building or structure is still in the design and construction phase you might only want to share important milestones within ArcGIS and replace the digital model.
You can work locally in ArcGIS Pro with BIM files or share them as web layers in ArcGIS Online or ArcGIS Enterprise. As web layers you can define read only layers are editable layers depending on your needs.
Required software
ArcGIS Pro is required to add a BIM file, inspect, edit, and author a building scene layer. You can view BIM models in ArcGIS Online and ArcGIS Enterprise.
| ArcGIS Pro version | Revit (Autodesk) Supported Version |
|---|---|
Pro 3.4 | Revit 2020 to 2025 |
Pro 3.3 | Revit 2019 to 2024 |
Pro 3.2 | Revit 2018 to 2023 |
ArcGIS help documentation
The following lists additional ArcGIS product resources:
- What is BIM data?
- BIM data as ArcGIS Pro layers
- Validation of CAD and BIM data positioning
- Building scene layer
- Explore building scene layers in ArcGIS Online
- What is a scene layer?
- Export a digital model to a geodatabase
- Use special paste to copy features in ArcGIS Pro
- Append features using geoprocessing
- Upgrade the Revit file version in ArcGIS Pro
ArcGIS blogs, stories, and technical papers
The following lists reference materials for ArcGIS products:
- Geolocate a Digital Model (Revit or IFC) in ArcGIS Pro
- ArcGIS Tools for BIM
- Geolocation Autocad\Civil 3D\Revit and ArcGIS Pro - Document
- Geolocation Autocad\Civil 3D\Revit and ArcGIS Pro
- Automation BIM for Digital Twin
- What’s new in CAD and BIM in the November 2024 release of ArcGIS Pro
- Modernize Infrastructure and Facility Operations with ArcGIS GeoBIM
Videos
The following lists Esri-produced videos that clarify and demonstrate concepts, software functionality, and workflows:
Tutorials
The following lists guided hands-on lessons based on real-world problems:
Esri community
The following lists online 3D community resources to connect, collaborate, and share experiences: