Drone2Map obtains GPS information from images or an external geolocation file during project setup. At times, projects may require better accuracy than the GPS can provide. For better precision, you can add control to your project. Control refers to points on the earth's surface with a known location that can be used to georeference your images to the correct position. Drone2Map provides the capability to import control from a file or manually add control from the map.
Note:
It is important to follow the following guidelines when working with control:
- You must include at least three control points for them to be taken into account during processing. A minimum of five control points is recommended.
- Between five and ten control points are recommended and are usually sufficient for most projects. More than ten are not typically required and do not significantly improve the accuracy of your results.
- In projects with complex topography, a higher number of control points will improve the accuracy of your results.
- While a minimum of two image links are required, five or more links are recommended.
- Control should be evenly distributed throughout your project area to minimize errors in scale and orientation.
- Do not place control points at the outer edges of the project area, as they will only be visible in a limited number of images.
Add control
If you have a file with control points for your project area, import them to Drone2Map or manually create your own.
Import from a CSV or text file
- On the Home tab, click the Control drop-down list.
- Click Import Control
 .
. - Choose to import from a CSV or text file.
- Click OK.
- In the Import Control window, click Browse, browse to the file with your control, and select it.
- Check the check box if the file contains headers and select the delimiter type. If your control file does not contain headers, map the field to the correct column in the control file.
- If necessary, update the Control Coordinate System.
- If necessary, update your control Vertical Reference.
See Vertical reference for help determining the correct inputs.
- Optionally, import your GCP photos.
- Click OK.
The list of control points from the external file appears in the Control Table.
Import from Drone2Map control export
Note:
GCP exports from a Drone2Map 1.x project cannot be imported into Drone2Map 2.x.- On the Home tab, click the Control drop-down list.
- Click Import Control
 .
. - Select Import from Drone2Map control export.
- Click OK.
- Browse to the control export .zip file and select it.
Control points from the file appear in the right pane and linked images appear in the left pane.
- Click OK to import control.
The list of control points from the export file appears in the GCP table.
Note:
Control imported from a previous Drone2Map export can only be used with the same images that were used when originally exported.
Import from feature class
- On the Home tab, click the Control drop-down list.
- Click Import Control
 .
. - Select Import from feature class.
- Click OK.
- Browse to the shapefile or the control point feature class and select it.
- Optionally, check the boxes to use feature geometry and z-values.
- If necessary, update the Control Coordinate System.
- If necessary, update your control Vertical Reference.
See Vertical reference for help determining the correct inputs.
- Optionally, import your GCP photos or use feature attachments if your feature class includes photo attachments.
- Click OK.
Import from a hosted feature layer
- On the Home tab, click the Control drop-down list.
- Click Import Control
 .
. - Select Import from hosted feature layer.
- Click OK.
- Select the folder that contains your hosted feature layer.
- Select the hosted feature layer containing your control.
- If your hosted feature layer contains multiple layers, click the Point Features drop-down list and select the correct layer.
- Optionally, check the boxes to use feature geometry and z-values.
- If necessary, update the Control Coordinate System.
- If necessary, update your control Vertical Reference.
See the Vertical reference page for help determining the correct inputs.
- Optionally, import your GCP photos or use feature attachments if your hosted feature layer includes photo attachments.
- Click OK.
Add from map
- On the Home tab, click the Control drop-down list.
- Click Add from Map
 .
. - Click an easily identifiable point on the imagery basemap or another image added from your portal.
To add more control from the map, click the Add Control button on the ribbon for each new control point.
Control type
Drone2Map allows you to set your control as a Ground Control Point (GCP) or Check Point.
Ground control points (GCPs) are used to georeference the model. If you have more GCPs in a project than necessary to accurately scale, rotate, and locate, some of the GCPs can be used as checkpoints to assess the accuracy of the project. GCPs improve the relative and the absolute accuracy of the model.
Checkpoints (CPs) are used to assess the absolute accuracy of the model. The image links for the checkpoints are used to estimate the model's 3D position as well as potential errors in the placement of the check points. This way, the relative accuracy in the area of the checkpoints may improve. The difference between the initial and the computed positions of the checkpoints is displayed in the Processing Report, and it gives an estimation of the absolute accuracy of the model in the region.
There are two ways to set your control type.
From the control tool
To set the control type using the control tool, complete the following steps:
- Select one or more control points.
- On the Home tab, click the Control drop-down list.
- Click Control Type
 .
. - In the Update Control Type window, choose Ground Control Point or Check Point from the drop-down list.
From the image links editor
To set the control type in the Image Links Editor, complete the following steps:
- On the Home tab, click the Image Links Editor button
 .
. - In the Control Point section in the upper right corner of the window, use the arrows to page through your control points until the desired control point is featured.
- Click the Control Point Type drop-down list and select the control type.
Export control
The Export Control tool allows you to save your control and associated linked images as an external file. This way, you can reuse them in future projects.
- To export your control, use the Select tool to select the control points you want to export.
- On the Home tab, click the Control drop-down list.
- Click Export Control
 .
. - Choose a location to save the .zip file.
Control files are exported from Drone2Map as .zip files.
- Click Save.
Note:
Control imported from a previous Drone2Map export can only be used with the same images that were used when originally exported.
Remove control
To remove control from your project, complete the following steps:
- Use the Select tool to select the control points you want to remove.
- On the Home tab, click the Control drop-down list.
- Click Remove Control
 .
. - Click Yes to confirm you want to remove the selected control.
Control Manager
The Control Manager displays information about your placed control points and provides quick access to common control operations.
To open the Control Manager, click the Control Manager button  on the Home tab.
on the Home tab.
Control operations
Use the Control Manager to access the following:
- Image links editor—See Image links editor for linking your control points with your images.
- Add control from map—See Add control from map for adding control points using a basemap.
- Import control—See Import control for importing control points from an external source.
- Remove control—See Remove control for removing select control points from your project.
- Filter control—Allows you to filter control points by type. To filter by control point type, click the Filter control drop-down list.
 in the Control Manager
and check all types that apply.
When a control point type is
not available, that filter will be disabled.
in the Control Manager
and check all types that apply.
When a control point type is
not available, that filter will be disabled. - Add manual tie points—In some situations, such as over water, automatic tie points may not be created. To assist in stitching together these areas, Drone2Map allows for the creation of manual tie points. A manual tie point is a control point that is marked in two or more images by the user only in the image links editor. It can be used to assess and improve the reconstruction accuracy of the model.
To create a manual tie point, complete the following steps:
- From the Control Manager, click the Add manual tie point button
 .
.A new manual tie point is added to the Control Manager table.
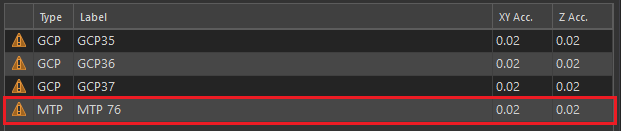
- Open the Image Links Editor.
- Select the manual tie point from the Control Manager table or from the Control Point drop-down list..
- Click an identifiable location in two or more images to mark the manual tie point.
Control information
The following table describes the attributes of the control information.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
Label | Displays the unique identifier for the control point. |
Type | Displays whether the control point type is GCP or Check Point. |
Latitude | Displays the latitude or y-coordinate of the GCP. |
Longitude | Displays the longitude or x-coordinate of the GCP. |
Elevation | Displays the elevation of the GCP. |
Image Links | Displays the number of linked images for a specific control point. The control point must be linked to at least two images. Linking to three to eight images is recommended. |
Accuracy Horizontal | Displays the horizontal accuracy in meters of the control point. |
Accuracy Vertical | Displays the vertical accuracy in meters of the control point. |
Image links editor
To apply control, links are created between each control point and corresponding images. Links can be created either manually or computer assisted. Manually linking control points to images is the preferred method when processing projects unattended, such as overnight processing, in which there is no intervention by the user throughout processing. Assisted linking of control points requires initial processing to be run, and significantly reduces the amount of time required to link control points to images.
Manual links
To create the image control links, complete the following steps:
- Import control, add control from the map, or add a manual tie point from the Control Manager.
- On the Home tab or in the Control Manager pane, click the Image Links Editor button
 .
.The image links editor opens and displays information about the selected control point, the control point type, and a list of the images on the left. The list of images is ordered by distance from the GCP or Check Point and in order of collection for manual tie points.
- In the images list, select an image to which the control should be linked.
The selected image appears in the preview window.
- Use the built-in map controls or your mouse to navigate the image. Use the rotate images buttons to orient the images to match the map. Place the crosshairs of the pointer in the image that corresponds to the control point and click to create or adjust the link.
A yellow X marks the point on the image. To redo the link, click another location. To remove the link, click Remove Link.
- To move to the next control point, select the control point from the Control Point drop-down list. Repeat steps 3 and 4 for each control point. Create a minimum of two links per image. Additional links are recommended for best results.
Assisted links
Drone2Map can estimate the location of control points in images after initial processing has completed, which can significantly decrease the time it takes to add control to your project.
Assisted image links are created using the dynamic mosaic. During the Initial processing phase, Drone2Map creates a dynamic mosaic by default. When an image link is applied to an image in the image links editor, the dynamic mosaic is queried, returning all images that share the image link coordinates.
Note:
You can add the dynamic mosaic to the map by selecting Add to map under Dynamic Mosaic on the 2D Product tab of the Options dialog box, or by accessing the dynamic mosaic directly from the project file geodatabase in the Catalog pane.
To create assisted image links, complete the following steps:
- Complete the Initial processing step.
- Import control, add control from the map, or add manual tie points.
- On the Home tab or in the Control Manager pane, click the Image Links Editor button
 .
.The image links editor opens and displays information about the selected control point, the control point type, and a list of the images on the left.
- In the images list, select an image to which the control should be linked.
The selected image appears in the preview window.
- Use the built-in map controls or your mouse to navigate the image. Use the rotate images buttons to orient the images to match the map. Place the crosshairs of the pointer in the image that corresponds to the control point and click to create or adjust the link.
A yellow X marks the point on the image. To redo the link, click another location. To remove the link, click Remove Link.
After placing the first image link for the current control point, Drone2Map estimate the location of image links for all remaining images of the currently selected control point and sort the images based on the accuracy of the estimated placement of the link. Estimated image links with a crosshair icon
 represent more accurate
estimations, while image links
marked with a circle icon
represent more accurate
estimations, while image links
marked with a circle icon  represent less accurate estimations. Only images with
estimated link locations will be displayed in the images
list.
represent less accurate estimations. Only images with
estimated link locations will be displayed in the images
list.Note:
Processing the Initial step at a higher keypoint image scale will increase the accuracy of automatic image links.
Note:
It is possible that the image to which you want to add an image link has an accuracy below the threshold to be listed in the image list. This is especially true when using MTPs to stitch together images that were not aligned during initial processing. In this case, you can check the Show all images check box to view images without estimations.
- In the image list, select the next image with an assisted image link icon.
- Review the location of the assisted image link.
- Repeat steps 4 through 7 until all image links have been reviewed, making adjustments where necessary.
- Once all images have been reviewed, click the Auto Link button to automatically link the remaining images with a crosshair icon that has not been manually linked.
- To move to the next control point, select the control point from the Control Point drop-down list. Repeat steps 4 through 9 for each control point. Create a minimum of two links per image. Additional links are recommended for best results.
Before Drone2Map can estimate the location of control points, you must first run the Initial processing step to create the dynamic mosaic. It is not necessary to process the Dense Point Cloud, 2D Products, or 3D Products. Selecting only the Initial processing step from processing options will minimize the time it takes to link control points.
When setting the Keypoints Image Scale in the Initial processing parameters, it is recommended that you choose a scale that matches the intended scale of your final product. Selecting a smaller scale will decrease the accuracy of automatic image links, and changing the scale on subsequent Initial processing will require Drone2Map to recalculate keypoints, increasing the overall processing time of your project. See Processing options for more detail about Initial processing.
The selected image
appears in the preview window with the estimated location of the
image link. More accurate estimations are marked with
a blue
crosshair  and less accurate
estimations with an orange crosshair
and less accurate
estimations with an orange crosshair  .
.
It may be necessary to adjust the location of the assisted image link. To adjust the image link, place the crosshairs of the pointer in the image that corresponds to the control point and click to adjust the link. The blue crosshair will change to a yellow X, indicating that the image link has been applied.
If you are satisfied with the location of the assisted image link, no adjustments are necessary.
If you have more GCPs than needed within the project area, optionally set some control as Check Points using the Control Point Type drop-down list at the top of the Image Links window.
Control photos
Taking photos of your GCPs during field collection provides a reminder of what each control looks like and makes it easier to properly mark the correct control during project setup. Drone2Map provides multiple ways to import your control photos along with your control points.
Manually import photos
You can add photos when importing from a CSV or text file, file geodatabase, or hosted feature layer and view the photos while linking your control with your drone images. To add your control photos using this method, complete the following steps:
Note:
When importing your control photos, control labels must match the control photo file name.
- After you have selected the import control method and clicked OK, click the Browse button in the Control Photos (optional) section of the Import Control window.
- Browse to the folder with your control photos, and click OK.
- Select whether the Control Photo Extension is included in the name of the control in your CSV or text file, feature class, or hosted feature layer. If your list of control does not include the photo extension, select the appropriate photo extension from the list.
- Complete the remainder of the steps from the appropriate section above to import your control.
When a control point is featured in the image links editor, you can switch the control photo on and off by clicking the photo button below the image links window navigation controls. When clicked, the control photo opens in a small window. Click the blue arrow to expand the window.
Import as attachments
Tools such as ArcGIS Collector allow you to add attachments to your features. When ArcGIS Collector is used to capture your control, Drone2Map allows you to import your photo attachments along with the control features when importing from a feature class or a hosted feature layer. During the import process, when you select a point feature class or hosted feature layer that has attachments, Use Features Attachments is checked by default. Leave it checked and Drone2Map will import your photo attachments to your project.