The Visual CGA Editor is a node-based programming interface that simplifies building procedural designs. It is based on a set of high-level architectural components and materials released with the ESRI.lib, designed to support a wide range of massing typologies usable across VCGA, CGA, and urban environments.
Download the VCGA Playground example to have access to the following:
- Multiple examples for VCGA design.
- A rich CGA component library. CGA components are nodes in a VCGA design; you can use the library to create your own designs.
Open CityEngine and click Help > Download Tutorials and Examples > Example VCGA Playground in the main menu. The Example VCGA Playground project is automatically downloaded and added to your CityEngine workspace.
You can also access the VCGA Playground example on ArcGIS Online. There are accompanying video tutorials to help get you started.
Visual CGA Editor
In the Visual CGA Editor window, you can write and modify VCGA designs which are identified by the .vcga extension. To edit a VCGA design, do the following:
- Open the VCGA design file:
- Double-click the design file in the Navigator window.
- If a selected object has a VCGA design file assigned, click Rule File in the Inspector window to open it.
- Edit the design.
The Visual CGA Editor automatically saves the VCGA design with every change and generates the 3D model if it is assigned to a selected shape in the Viewport window. This means there is no need to manually save and generate the VCGA design.
Visual CGA Editor nodes
The Visual CGA Editor utilizes a node-based system in which nodes are connected to implement procedural designs.
To add nodes, double click anywhere in the Visual CGA Editor window, or right-click in the window and select Add Node. This opens the Add Node dialog box:
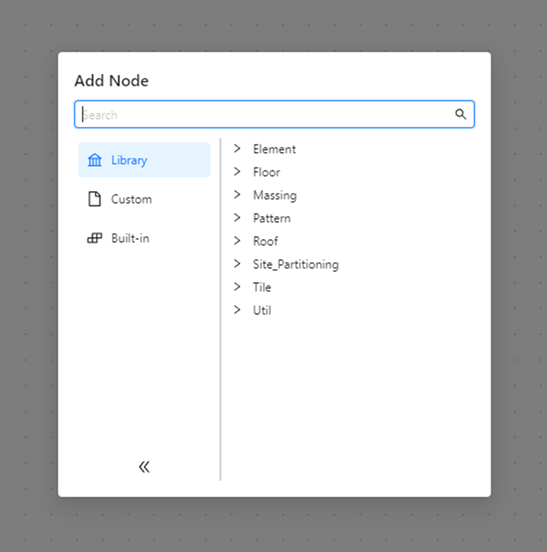
The Add Node dialog box has the following types of nodes:
- Library—Displays the architectural components provided by the ESRI.lib.
- Custom—Displays the custom components located in the rules folder of the current project.
- Built-in—Displays the built-in nodes provided by the editor, such as value, attribute, extension, and conditional nodes.
This layout helps you to quickly find and use different types of nodes to build your procedural designs efficiently.
Component nodes
Each component node in the Visual CGA Editor window corresponds to either a CGA or a VCGA file. You can directly open this file using the Open Component File option in the node context menu that displays when you right-click the node.
Body

Each node has input and output slots in which circular slots represent values and square slots represent shapes. These can further be categorized into four distinct slot types:
- Input shape slot—This slot represents the input shape of the component.
- Extension slots—These slots represent the extension point shapes of the component.
- Empty white slots mean that no geometry is generated for that extension unless it is connected to another node, while filled black slots mean a shape for this extension will be generated by default.

- Empty white slots mean that no geometry is generated for that extension unless it is connected to another node, while filled black slots mean a shape for this extension will be generated by default.
- Extension parameter slots—These slots represent the extension point parameter of the component. These parameters forward shape specific values.
- Attribute slots—These slots represent the input parameters of the component. Each slot allows you to set a value in two ways:
- You can create a value or attribute node and connect it to the slot.
- You can use the mini-inspector pop-up that opens when you click Edit
 when hovering over the slot. Initially, every attribute slot uses the default value of the component, but you can set new values. Default values are only evaluated at run time and cannot be displayed. However, default attribute values can be reviewed in the Inspector window (see below).
when hovering over the slot. Initially, every attribute slot uses the default value of the component, but you can set new values. Default values are only evaluated at run time and cannot be displayed. However, default attribute values can be reviewed in the Inspector window (see below).
Slots can be hovered to show their description in a tooltip.
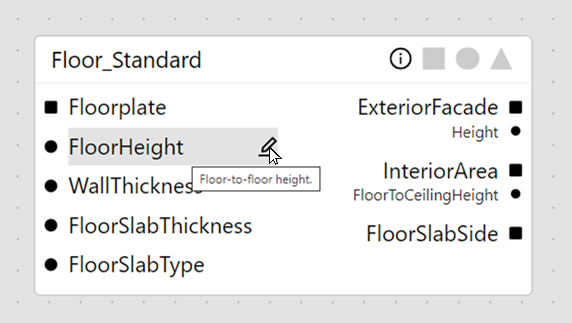
Title bar
In the component node’s title bar, you can use buttons that have the following functionalities:
- The
 button displays the description of the component.
button displays the description of the component. 
- The square toggle button turns a component on or off. Turning a component off prevents its shape from being generated.

- The circular button makes the attributes visible in the Inspector window.

- The triangular button enables visualization of the input shapes' scopes on the lead selection in the Viewport window.

Visualization
You can select a component node to highlight its extension points on the lead selection in the Viewport window:

It is also possible to highlight a single extension point by hovering over the corresponding output slot. This feature is useful for visually identifying specific extension points in the Viewport window.
Built-in nodes
In the Visual CGA Editor window, you can use built-in nodes such as the attribute, value and conditional nodes to have better control over how component nodes are evaluated in a VCGA design.
InitialShapes node
This node is the root of the visual graph, and it cannot be deleted or cloned. It represents the shapes that the rule is assigned to in the scene. The @-button in the title bar of the node opens the annotation editor where you can provide a description for the VCGA design as well as a description for the InitialShapes node itself.
Value nodes
These nodes provide a constant value as an output.
Attribute nodes
These nodes define the attributes of the VCGA design and are displayed in the Inspector window.
Attribute nodes can be created automatically by dragging a connection from an attribute slot and dropping it onto the canvas. This action opens the drop-down context menu, which includes the Link attribute in the Inspector option.
Attribute nodes provide an output value that can be initialized to a custom value or to the default value of a connected attribute slot of a component. However, a user-set value in the Inspector window always has precedence.
When attribute nodes are initialized to the default value of an attribute slot, they also inherit their annotations. Conversely, when attributes nodes specify a custom value, they allow for the configuration of custom annotations through the annotation editor.
The @ button in the title bar of the node opens the annotation editor. In this editor several preferences can be configured that influence how the attribute is presented in the Inspector window and the Visual CGA Editor window.

Extension nodes
These nodes specify the extension points of the VCGA design. They become visible as extension slots when the Visual CGA design is used as a component in another Visual CGA design.
A default shape is generated for the extension node.
The following are the options for setting the default shape of an extension node:
- Identity: Keep the input geometry as-is.
- NIL: Generate no geometry by default.
- Extension name (default): Generate the same default geometry as the selected extension.
Switch nodes
Switch nodes enable the activation and deactivation of different branches within the visual graph through custom properties.
Conditional nodes
Conditional nodes allow the user to direct the shape flow by comparing attribute, value or parameter connections.

Visual CGA Editor toolbar

The Visual CGA Editor toolbar includes the following tools:
Select and frame | Select and frame objects in the Viewport window with the current VCGA design assigned. |
Assign | Assign the current VCGA design to the selected objects in the Viewport window. |
Export | Export the current Visual CGA design as CGA rule file. |
Frame | Frame the selected nodes (F), or frame all if nothing is selected. |
Zoom in | Zoom / Dolly in. |
Zoom out | Zoom / Dolly out. |
Find Node | Open a search dialog to find a node by its title (Ctrl+F). Clicking on a node title will frame the view to the selected node. |
Toggle mini-map | Toggle the mini-map in the editor. |
Creating Custom Components
Any Visual CGA Design can be integrated as custom component into another Visual CGA Design where the InitialShapes node becomes the input shape slot, attribute nodes become attribute slots and extension nodes become extension slots.
Further, a CGA Rule File itself can be configured as custom component. A CGA component must contain a start rule which serves as the input shape slot. Attributes serve as attribute slots and extension rules serve as extension slots. Their parameters will be displayed as extension parameter slots. A component can be documented with @RuleFileDescription annotation. Start rule, attributes and extension rules can be documented using the @Desciption annotation.
@RuleFileDescription("
This text describes the function of the component.
It will be displayed when pressing the (i) button on a component node.
- this text will automatically be formatted using markdown
")
@Description("This will be displayed when hovering the extension slot in VCGA")
extension My_Extension(My_Extension_Parameter) --> My_Extension.
@Description("This will be displayed in the inspector
and when hovering the attribute slot in VCGA")
attr My_Attribute = 0
@Description("This will be displayed when hovering the start shape slot in VCGA")
start My_Start_Rule_Name -->
My_Extension(My_Attribute)

Manage rule errors
Errors in the VCGA file are detected automatically and are marked differently based on the type of error.
Component node errors
Component nodes can show the following possible error states:
- Error: the file *** has changed—Reload the node to resolve: This error indicates that the CGA/VCGA file linked to the component node has been modified, altering its signature (e.g., attributes or extensions have been introduced, modified, or removed). The error can be fixed using the Reload Node option in the context menu.
- Error: the file *** contains errors—This error indicates that the CGA/VCGA file linked to the component node contains errors. This can be fixed by manually fixing the errors inside the respective CGA or VCGA file.
- Error: the file *** could not be found—This error occurs when the CGA/VCGA file linked to the component node has been deleted or renamed. It can be fixed by selecting Change Component File from the context menu.
Input node errors
Input nodes validate the entered values. If validation fails, an error is displayed based on the node's type. An explanatory pop-up provides details about why the validation failed.

VCGA file errors
When there are compilation errors within the VCGA file, a small red cross appears in the window tab:

More detailed information about the error can be found in the Problems window (Window > Problems). Errors must be resolved before applying the rules. It is not possible to generate models if the assigned rule file contains errors.
Shortcuts
In the Visual CGA Editor window, you can use navigation and keyboard shortcuts to work more efficiently.
You can configure the global navigation mouse scheme in the CityEngine preferences. This allows customizing nodes selection, panning (scrolling), and zooming shortcuts.
You can use the following keyboard shortcuts when working in the Visual CGA Editor window:
Ctrl+Z | Undo |
Ctrl+Y | Redo |
Ctrl+A | Select all nodes |
Ctrl+C | Copy selection to clipboard |
Ctrl+V | Paste clipboard to canvas |
Ctrl+F | Open Find Node dialog |
F | Frame the selected nodes, or frame all if nothing is selected |
Space | Maximize or minimize the Visual CGA Editor window |







