Get map data from ArcGIS Online and ArcGIS Enterprise to add context, such as streets, footprints, terrain, and basemaps, to a new or existing CityEngine scene.
To use the Get Map Data tool, sign in to your account and do one of the following:
- Select Create a city from map data from the CityEngine welcome screen to create a new scene from downloaded data.
- Select File > Get Map Data from the main menu to import downloaded data into an existing scene.
Download data
To download map data into CityEngine, follow these steps:
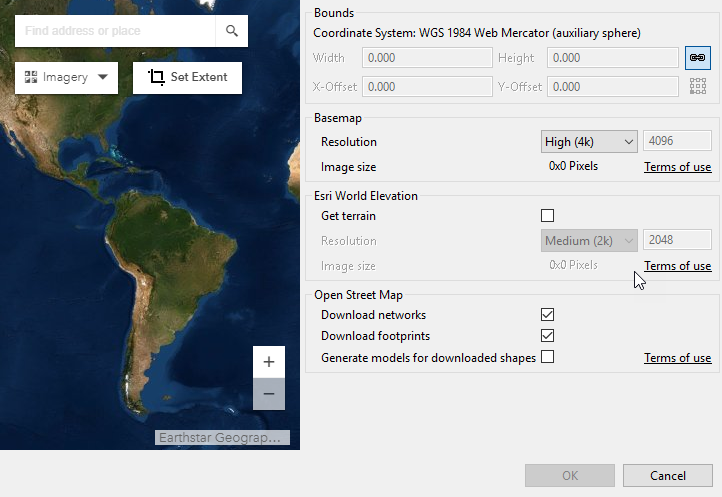
- Navigate to the area of interest.
- Click Set extent
 to specify the extent of the downloaded data.
to specify the extent of the downloaded data.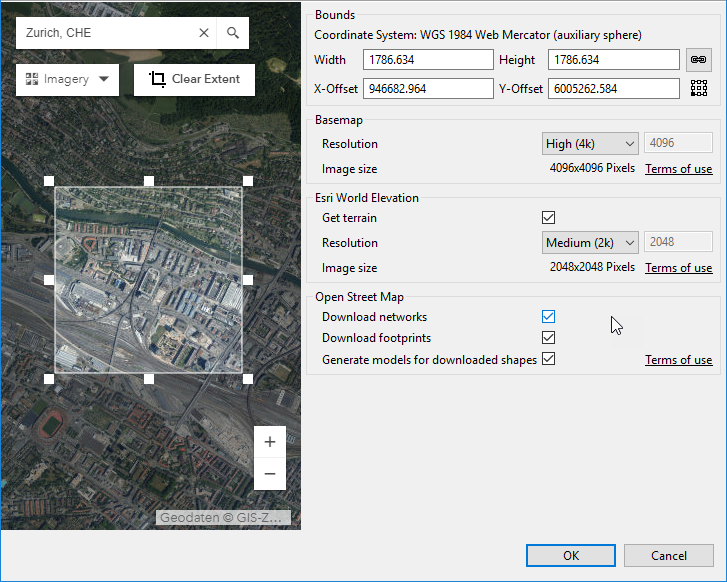
The extent is set for Zurich, Switzerland You can also do any of the following:
- Change the size and location by adjusting the rectangle.
- Click Clear Extent
 to remove the extent.
to remove the extent. - Search for a location.
- Click Select Basemap
 to change the type of basemap from the drop-down menu.
to change the type of basemap from the drop-down menu.
Note:
- There are minimum and maximum limits for the extent.
- The settings are disabled until you set an extent.
- In an existing CityEngine scene, if an extent is farther than 500 kilometers from the scene, a red rectangle appears. CityEngine displays an error at the top to inform you to change the location of the extent or create a new scene.
- Specify the settings for the downloaded data. See Get map data settings for more information.
- Click OK.
- If you choose to download OpenStreetMap (OSM) data, an additional dialog box appears on which you can configure the OSM settings. When the OSM dialog box appears, you have the choice to accept the default settings and click Finish or to click Next and review the settings of each option you checked.
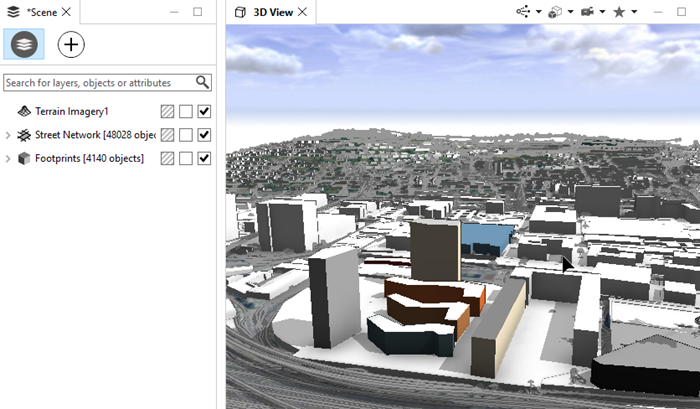
- Map imagery, elevation, and OSM data, such as building footprints and streets, are downloaded according to your settings.
- All data is added to your scene. For your convenience, default rules from ESRI.lib are assigned to the OSM data (see OpenStreetMap for more information).
- Data is saved to the /maps folder of your current project.
Tip:
The following is some basic information to help you improve the quality of the OSM network data imported into CityEngine:
- The graph networks are usually contained in the highway layer in the layer list of the OSM dialog box.
- You can expand the highway layer and select or deselect the different network types. For example, you may want only the major streets in your scene.
- After running the tool, the graph networks are merged into one graph layer in CityEngine.
- You can import the map.osm file located in the project/maps folder multiple times. This allows you to add the highway layer a number of times into CityEngine and create different graph layers to give you greater control of the OSM network data.
- After the OSM data is added to the scene, it is often needed to manually clean up the networks to improve the quality of the data.
See the Import OSM street data section in Tutorial 4: Import Streets for more information.
Get map data settings
The Get Map Data tool includes the following options:
Bounds |
|
Basemap |
Note:The ratio of the image size dimensions matches the ratio of the extent width and height. Therefore, the image size dynamically changes as the extent size changes. |
Esri World Elevation | Esri provides a comprehensive elevation map of the world offering terrain at different scales. See Elevation Coverage Map for more information.
Note:Elevation data is only available for subscribed users or those with an organizational ArcGIS Online account. |
Open Street Map |
Caution:You may experience long download times if the extent is too large. |
 —Maintains the aspect ratio when manually entering values.
—Maintains the aspect ratio when manually entering values. —Specifies which vertex of the extent rectangle to reference for the x- and y-coordinates.
—Specifies which vertex of the extent rectangle to reference for the x- and y-coordinates.