| Label | Explanation | Data Type |
Input Layer | The point, line, or polygon features that will be grouped. | Feature Layer |
Output
| The output feature class with grouped features represented by a new field named group_id. | Feature Class |
Spatial Relationship | Specifies the type of relationship that features will be grouped by.
| String |
Spatial Near Distance (Optional) |
The distance that will be used to group near features. This parameter is only used when the Spatial Relationship parameter value is Planar Near or Geodesic Near. | Linear Unit |
Temporal Relationship (Optional) | Specifies the time criteria that will be used to match features. When the parameter is set to Intersects or Near, features are grouped when both the spatial and time criteria are met. Time must be enabled on the input to support this option.
| String |
Temporal Near Distance (Optional) |
The temporal distance that will be used to group near features. This parameter is only used when the Temporal Relationship parameter value is Near. | Time Unit |
Attribute Relationship
(Optional) | An ArcGIS Arcade expression that will be used to group features by. For example, $a["Amount"] == $b["Amount"] groups features when the Amount field has the same value. | String |
Summary
Groups features that are within spatial or spatiotemporal proximity to each other.
The following are examples of questions that can be answered by Group By Proximity workflows:
- Which roads are connected?
- Where are there groups of crime that happened within a close distance and time of each other?
- Are there groups of polygons that overlap each other?
Illustration
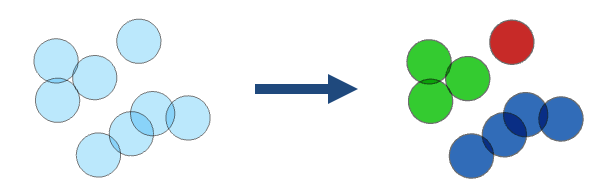
Usage
The output result is a copy of the input with a new field named group_id. The group_id field represents the grouping of features. Features with the same group_id value are in the same group. The group numbers represent membership in a particular group and don't imply value. The group numbers may not be sequential or the same number in repeat use of the tool. Results will be symbolized with eight groups. If there are more than eight groups in the result, all groups will be symbolized with eight colors by default. You can modify the symbology to show each unique group by symbolizing with unique symbols on the group_id field.
The tool supports the following combinations of relationships:
- A spatial relationship
- A spatial relationship and a temporal relationship
- A spatial relationship and an attribute relationship
- A spatial relationship, a temporal relationship, and an attribute relationship
The supported spatial relationships and input geometries are described in the following table:
Input geometry type Intersects Touches Geodesic Near Planar Near Point



Polyline




Polygon




Overlay method Description Intersects
Features intersect when features or portions of features overlap. This is the default.
Touches
Features touch another feature if they have an intersecting vertex, but the features do not overlap.
Geodesic Near
Features are near if a vertex or edge is within a given geodesic distance of another feature.
Planar Near
Features are near if a vertex or edge is within a given planar distance of another feature.
To use the Spatial Relationship parameter's Planar Near option, the Input Layer parameter value must be projected or the output coordinate system is set to a projected coordinate system.
The supported temporal relationships and temporal types are described in the following table:
Input temporal type Intersects Near None
Instant


Interval


Temporal relationship method Description Intersects
Features intersect when any part of a feature's time overlaps another.
Near
Features are near one another if a feature's time is within a given time distance of another feature.
To use a temporal relationship, you must enable time on the input. You can enable time by doing the following:
- Enable time on a multifile feature connection (MFC) input.
- Enable time on a layer in the map. You can optionally save the time-enabled layer as a .lyrx file.
Attribute expressions are a symmetric operation. The tool takes a single input layer that is compared to itself when grouping. Because of this, the input layer is denoted as both a and b in the ArcGIS Arcade expression, and all expressions need to include both a and b. For example, to group all records when the Amount field has the same value, use the following expression: $a["Amount"] == $b["Amount"].
You can improve performance of the Group By Proximity tool by doing one or more of the following:
- Set the extent environment so that you only analyze data of interest.
- When using the Spatial Relationship parameter's Planar Near or Geodesic Near option, use a smaller Spatial Near Distance parameter value.
- When using the Spatial Relationship parameter, the Planar Near option is faster than the Geodesic Near option.
- When using the Temporal Relationship parameter's Near option, use a smaller Temporal Near Distance parameter value.
- Use data that is local to where the analysis is being run.
This geoprocessing tool is powered by Spark. Analysis is completed on your desktop machine using multiple cores in parallel. See Considerations for GeoAnalytics Desktop tools to learn more about running analysis.
When running GeoAnalytics Desktop tools, the analysis is completed on your desktop machine. For optimal performance, data should be available on your desktop. If you are using a hosted feature layer, it is recommended that you use ArcGIS GeoAnalytics Server. If your data isn't local, it will take longer to run a tool. To use your ArcGIS GeoAnalytics Server to perform analysis, see GeoAnalytics Tools.
Parameters
arcpy.geoanalytics.GroupByProximity(input_layer, output, spatial_relationship, {spatial_near_distance}, {temporal_relationship}, {temporal_near_distance}, {attribute_relationship})| Name | Explanation | Data Type |
input_layer | The point, line, or polygon features that will be grouped. | Feature Layer |
output | The output feature class with grouped features represented by a new field named group_id. | Feature Class |
spatial_relationship | Specifies the type of relationship that features will be grouped by.
| String |
spatial_near_distance (Optional) |
The distance that will be used to group near features. This parameter is only used when the spatial_relationship parameter value is NEAR_PLANAR or NEAR_GEODESIC. | Linear Unit |
temporal_relationship (Optional) |
Specifies the time criteria that will be used to match features. When the parameter is set to INTERSECTS or NEAR, features are grouped when both the spatial and time criteria are met. Time must be enabled on the input to support this option.
| String |
temporal_near_distance (Optional) |
The temporal distance that will be used to group near features. This parameter is only used when the temporal_relationship parameter value is Near. | Time Unit |
attribute_relationship (Optional) | An ArcGIS Arcade expression that will be used to group features by. For example, $a["Amount"] == $b["Amount"] groups features when the Amount field has the same value. | String |
Code sample
The following Python window script demonstrates how to use the GroupByProximity function.
# Name: GroupByProximity.py
# Description: Group roads together that touch
#
# Requirements: An advanced license
# Import system modules
import arcpy
# Set local variables
inFeatures = "C:\myData\cities.gdb\roads"
outname = "groupedRoads"
overlayType = "TOUCHES"
# Run Group By Proximity
result = arcpy.gapro.GroupByProximity(inFeatures, outname, overlayType)