| Label | Explanation | Data Type |
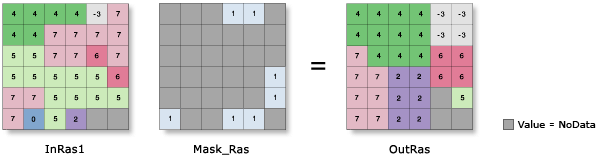
Input raster | The input raster with the masked locations that will be replaced by the value of their nearest neighbor. The input raster can be either integer or floating point type. | Raster Layer |
Input raster mask | The raster that identifies the locations in the input raster that will be replaced. Cells with a value of NoData are considered to be within the masked area. In the output raster, these locations will be replaced by the value of their nearest neighbor in the Input raster value. The mask raster can be either integer or floating point type. | Raster Layer |
Use NoData values if they are the nearest neighbor (Optional) | Specifies whether NoData cells in the input raster can replace cells in the masked areas if they are the nearest neighbor.
| Boolean |
Nibble NoData cells (Optional) | Specifies whether NoData cells in the input raster that are within the masked area will be preserved or replaced.
| Boolean |
Input zone raster (Optional) | The input zone raster. For each zone, input cells that are within the mask will be replaced only by the nearest cell values within that same zone. A zone is all the cells in a raster that have the same value, whether or not they are contiguous. The input zone layer defines the shape, values, and locations of the zones. The zone raster can be either integer or floating point type. | Raster Layer |
Return Value
| Label | Explanation | Data Type | Output raster | The output raster with the replaced cells. The identified input cells will be replaced with the values of their nearest neighbor. If the in_raster value is integer, the output raster will be integer. If it is floating point, the output will be floating point. | Raster |