


Note:
ArcGIS Insights is deprecated and will be retiring in 2026. For information on the deprecation, see ArcGIS Insights deprecation.
Line graphs show information as a series of data points that are connected by straight line segments. Categories are shown along the x-axis, and statistics are shown along the y-axis. Unlike time series graphs, which only use date and time along the category axis, line graphs allow you to use string fields along the category axis.
Line graphs can answer questions about data, such as: How are numeric values distributed or summarized by category?
Example
An environmental organization is tracking the drought conditions in Southern California and wants to compare precipitation levels across the region to determine which cities are most vulnerable. The organization uses a line graph to show the total precipitation for each city.
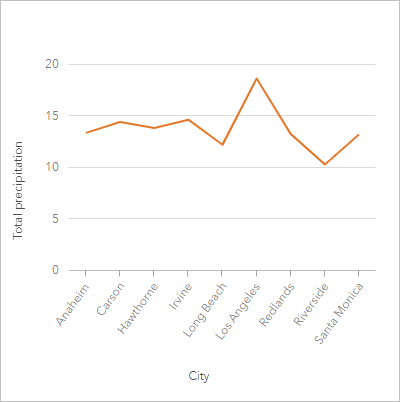
Create a line graph
To create a line graph, complete the following steps:
- Select one of the following combinations of data:
- One or two string fields

- One or two string fields
 and a number field
and a number field  or a rate/ratio field
or a rate/ratio field 
Note:
If you do not select a number or rate/ratio field, the data will be aggregated and a count will be displayed.
You can search for fields using the search bar in the data pane.
- One or two string fields
- Create the chart using the following steps:
- Drag the selected fields to a new card.
- Hover over the Chart drop zone.
- Drop the selected fields on Line Graph.
Tip:
 Drag a matching string field from a second dataset onto your line graph to create a combo chart.
Drag a matching string field from a second dataset onto your line graph to create a combo chart.
Tip:
You can also create charts using the Chart menu above the data pane or the Visualization type button  on an existing card. For the Chart menu, only charts that are compatible with the data selection will be enabled. For the Visualization type menu, only compatible visualizations (including maps, charts, or tables) will be displayed.
on an existing card. For the Chart menu, only charts that are compatible with the data selection will be enabled. For the Visualization type menu, only compatible visualizations (including maps, charts, or tables) will be displayed.
Usage notes
This visualization creates a result dataset  in the data pane, which includes the fields used to create the chart. The result dataset can be used to create additional visualizations, rename the fields on the chart axes or in the pop-ups, or apply filters to the chart.
in the data pane, which includes the fields used to create the chart. The result dataset can be used to create additional visualizations, rename the fields on the chart axes or in the pop-ups, or apply filters to the chart.
The trends for the line graph can be symbolized as a count of features over time or as a number or rate/ratio field. If a field is used, the values in the trend line can be calculated as the sum, minimum, maximum, average, percentile, or median of values from the field for each point in time.
Note:
Median and percentile are not available for certain remote feature layers. If the remote feature layer does not support median or percentile, you can copy the layer to your workbook.
An optional Subgroup field can be selected on the x-axis. The Subgroup field must be a string field and will be used to create separate lines for each subcategory.
Tip:
You can style related maps with the same field you used to group the chart. When you interact with the chart or map, you can see simultaneous categorical and spatial patterns.
Use the Layer options button  to open the Layer options pane and do the following to update the configuration options:
to open the Layer options pane and do the following to update the configuration options:
Use the Legend tab
To change the color or pattern associated with a value, click the symbol and choose a color from the palette, provide a hexadecimal value, or select a pattern. Changing the symbol on the Legend tab is only available for unique symbols. to view the symbols on the chart. The pop-out legend button
to view the symbols on the chart. The pop-out legend button  displays the legend as a separate card on the page. You can use the legend to make selections on the chart (available for unique symbols).
displays the legend as a separate card on the page. You can use the legend to make selections on the chart (available for unique symbols).Use the Symbology tab
Labels display the number values associated with the chart. The following configurations are available for labels: to apply the Smooth line parameter and turn labels on or off. A smooth line is best in situations when you are displaying trends in your data without sudden changes, rather than when you want to see specific values. For example, showing trends in monthly temperature using a smooth line is an effective way to analyze seasonality.
to apply the Smooth line parameter and turn labels on or off. A smooth line is best in situations when you are displaying trends in your data without sudden changes, rather than when you want to see specific values. For example, showing trends in monthly temperature using a smooth line is an effective way to analyze seasonality.- Decimal places—You can choose a number of decimal places from zero to five, or choose Default or Auto for the labels. The Default option abbreviates large numbers, and the Auto option assigns an appropriate precision.
- Label alignment—Three alignment options are available for line graphs: Horizontal, outside,Vertical, outside, and Angled.
- Context label—Characters, such as a symbol or unit, can be added to the label. The context label can be placed on either side of the value.
- Use the Appearance tab
 to change the symbol color (single symbol only) and change the pattern and thickness of the line.
to change the symbol color (single symbol only) and change the pattern and thickness of the line.
Use the Chart statistics button  to display the average, median, upper quartile, lower quartile, or a custom value.
to display the average, median, upper quartile, lower quartile, or a custom value.
Use the Card filter button  to remove any unwanted data from the card, or to show only the top or bottom n values. Filters can be applied to all string, number, rate/ratio, and date/time fields. A card filter does not affect other cards using the same dataset.
to remove any unwanted data from the card, or to show only the top or bottom n values. Filters can be applied to all string, number, rate/ratio, and date/time fields. A card filter does not affect other cards using the same dataset.
Use the Selection tools button  to select features on the chart using the single select tool, or invert the selection.
to select features on the chart using the single select tool, or invert the selection.
Use the Visualization type button  to switch directly between a line graph and other visualizations, such as a summary table, column chart, or bubble chart.
to switch directly between a line graph and other visualizations, such as a summary table, column chart, or bubble chart.
Use the Sort button  to change the sort order of the chart. The chart can be sorted in ascending, descending, alphabetical, or reverse alphabetical order. The default order is alphabetical (Sort A to Z).
to change the sort order of the chart. The chart can be sorted in ascending, descending, alphabetical, or reverse alphabetical order. The default order is alphabetical (Sort A to Z).
Use the Maximize button  to enlarge the card. Other cards on the page will be reduced to thumbnails. The card can be returned to its previous size using the Restore down button
to enlarge the card. Other cards on the page will be reduced to thumbnails. The card can be returned to its previous size using the Restore down button  .
.
Use the Enable cross filters button  to allow filters to be created on the card using selections on other cards. Cross filters can be removed using the Disable cross filters button
to allow filters to be created on the card using selections on other cards. Cross filters can be removed using the Disable cross filters button  .
.
Use the Flip card button  to view the back of the card. The Card info tab
to view the back of the card. The Card info tab  provides information about the data on the card, the Export image tab
provides information about the data on the card, the Export image tab  allows users to export an image of the card, and the Export data tab
allows users to export an image of the card, and the Export data tab  allows users to export the data from the card.
allows users to export the data from the card.
Use the Card options button  to access the following options:
to access the following options:
- Appearance button
 —Change the background color, foreground color, and border of the card.
—Change the background color, foreground color, and border of the card. - Edit labels button
 —Create custom labels for the chart axes. To edit the labels, click the Edit labels button and click the axis to make it editable.
—Create custom labels for the chart axes. To edit the labels, click the Edit labels button and click the axis to make it editable. - Order button
 —Move the card forward or move the card backward relative to other cards on the page.
—Move the card forward or move the card backward relative to other cards on the page. - Delete button
 —Remove the card from the page. If you did not intend to delete the card, you can retrieve it using the Undo button
—Remove the card from the page. If you did not intend to delete the card, you can retrieve it using the Undo button  .
.
Resources
Use the following resources to learn more about charts: