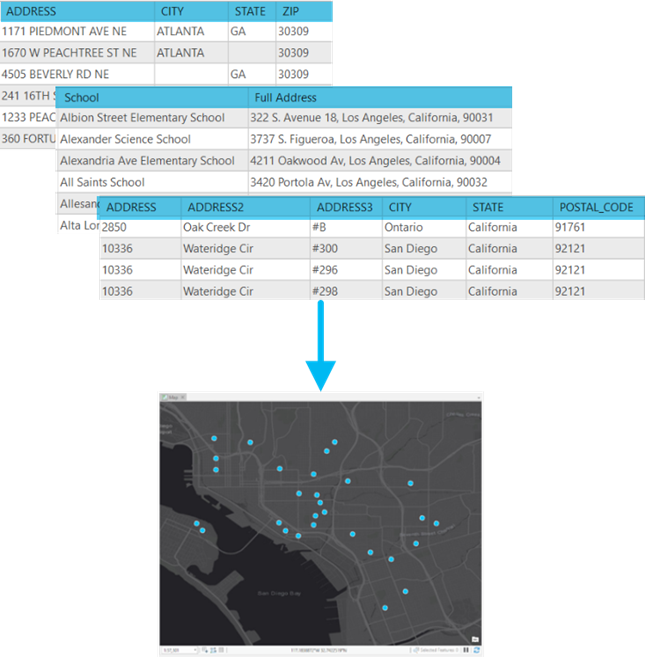
To geocode a table of addresses using the Geocode Table pane in ArcGIS AllSource, complete the following steps:
- Add the table you want to geocode to the map.
- Expand the Add Data drop-down menu
 on the Map tab on the ribbon, and click Data.
on the Map tab on the ribbon, and click Data. - Browse to the table, and double-click it to add it to the map.
The table is listed in the Contents pane.
- Expand the Add Data drop-down menu
- Open the Geocode Table pane, and begin the guided workflow.
- Right-click the table in the Contents pane of the map, and choose Geocode Table.
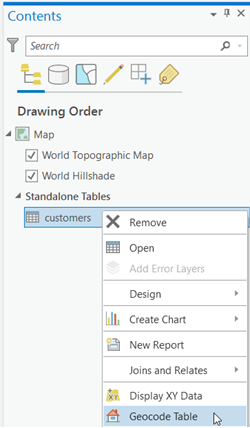
The Geocode Table pane appears. It displays a list of steps to use to geocode the table.
- Click Start.
The guided workflow begins.
- Right-click the table in the Contents pane of the map, and choose Geocode Table.
- Complete the About your table step of the guided workflow.
- Confirm that the correct table is displayed in the Input Table text box.
- Answer the question regarding the number of fields you want to geocode in your data, and select the corresponding option in the drop-down menu.
If you are unsure of the number of fields that need to be geocoded, click the Attribute table button
 to view the table.
to view the table. - Click Next.
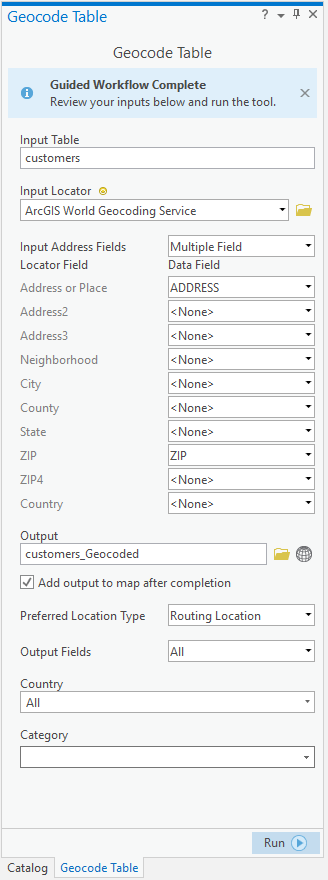
- Complete the What locator are you using? step of the guided workflow.
- From the Input Locator drop-down menu, choose the input locator you want to use for geocoding.
Locators added to the project that support batch geocoding automatically appear in the Input Locator drop-down menu of the Geocode Table pane, or you can browse to a different locator by clicking the Browse button
 .
. Note:
Performing geocoding operations using the ArcGIS World Geocoding Service requires an ArcGIS Online organizational subscription, and it consumes credits. The organizational account must have enough credits to complete the entire geocoding request.
Note:
Credit estimation is available at the top of the tool when the active portal is ArcGIS Online and the input locator is the ArcGIS World Geocoding Service.
- Click Next.
- From the Input Locator drop-down menu, choose the input locator you want to use for geocoding.
- Complete the Mapping the fields in your table step of the guided workflow.
- For each of the fields in your data that you want to use in geocoding, find the corresponding locator field and choose the appropriate data field in the drop-down menu.
The field mapping is completed automatically, but you should review the field mapping to ensure that you do not want to make any changes or map additional fields.
To review the fields in your data that need to be geocoded, click the Attribute table button
 to view the table.
to view the table. - Click Next.
- For each of the fields in your data that you want to use in geocoding, find the corresponding locator field and choose the appropriate data field in the drop-down menu.
- Complete the Output step of the guided workflow.
An output location and name are assigned automatically.
- To change the output, click the Browse button
 . Then, you can either select a new location or change the name.
. Then, you can either select a new location or change the name.Note:
Depending on the locator type you chose for geocoding, the output may be limited to either a location on disk or a location on your active portal. However, you can still change the name or the location in the folder structure of your designated output location.
By default, the output feature class is created using the same spatial reference as the locator. Optionally, to create the output feature class using a different spatial reference, click the Select coordinate system button
 and choose an output coordinate system.
and choose an output coordinate system. - Optionally, check the Add output to map check box after completion.
Depending on the size of the table and the location of output, this operation may be time-consuming.
- Choose an option for Preferred Location Type from the available drop-down menu.
When performing geocoding, you can use the geocoding results to display on a map or for further analysis. In this case, change the Preferred Location Type setting to Address Location so that the points represent the rooftop or parcel centroid for the address. The point that is displayed is closest to the center of the feature that represents the address. By contrast, you can use the geocoding results in a routing application in which you want the points to be located on the side of the street for better routing. In this case, Routing Location is the better option. With this option, the point that is displayed is typically closer to the street and closer to where a vehicle would arrive at the location.
- Optionally, specify an option other than the default All option from the Output Fields drop-down menu.
When you choose All, all of the table's original fields plus all fields generated by the geocoding process in the output feature class are included. Choose All to include all of the table's original fields with their original field names, plus all fields generated by the geocoding process in the output feature class. Choose Minimal to include all of the table's original fields plus the subset of fields generated by the geocoding process that are required for using the Rematch Addresses pane in the output feature class. Choose Minimal and User Fields to include all of the table's original fields, the subset of fields generated by the geocoding process that are required for using the Rematch Addresses pane, and user-defined output fields in the output feature class. Choose Location only to include all of the table's original fields plus a Shape field containing the geometry of the result in the output feature class. For a description of the output field options see what's included in the geocoded results.
Note:
If you geocode the table with the Location only option, you must select the locator you want to use for rematching the output feature class in the locator view of the Rematch Addresses pane and map the Input Address Fields again. - Click Next.
- To change the output, click the Browse button
- Optionally, complete the Limit by Country step of the guided workflow.
- If available, choose any combination of countries from the displayed list.
The capability to limit geocoding by country is determined by the locator you chose and is not always available. If the locator does not support the Country setting, this page of the guided workflow does not appear.
When using the World Geocoding Service or other locators that support multiple countries, you can specify that geocoding only occur in specific countries. This is important because it can improve geocoding performance and reduce the potential for an address to false-positively match in another country. It is possible for an address in one country to look similar to an address in another country. Geocode Table allows you to choose one or more countries to limit the results of the geocoding. In some cases, your table may contain addresses for many countries, in which case you should have a country field in the data and map that field in the field mapping section of the tool as opposed to selecting multiple countries in this step. Mapping a country field from the table will help to pinpoint the country for each record.
- Click Next.
- If available, choose any combination of countries from the displayed list.
- Optionally, complete the Limit by category step of the guided workflow.
- If available, choose any combination of categories from the displayed list.
The capability to limit geocoding by category is determined by the locator you chose and is not always available. If the locator does not support the Category setting, this page of the guided workflow does not appear.
You can limit the results of geocoding to specific categories, such as only address matches, because the geocoding results are for parcel delivery. Another example is if you know that the entire table consists of cities, and you don’t want New York to match New York State or even New York County. Using this parameter limits matches to a specific type of location.
- If available, choose any combination of categories from the displayed list.
- Review all inputs in the final step of the guided workflow, and run Geocode Table.
- Confirm that all the inputs on the final page of the guided workflow display the inputs you chose in the previous steps.
- Click Run.
The progress of the tool is displayed at the bottom of the pane.
If you selected the Add output to map option in the Output step of the guided workflow, the output is added to the map automatically.
Once you have a geocoded feature class, you can optionally add individual geocoding results from the Locate pane.
To review or change any of the results, add the feature class to the map if necessary, right-click the new feature class in the Table of Contents pane, and click Data > Rematch Addresses  .
.
Note:
You can also batch geocode a table of global coordinates (latitude/longitude, MGRS, DD, or USNG) using any locator created with the Create Locator tool or Create Feature Locator tool and ArcGIS StreetMap Premium locators. Support for coordinate searching is disabled or enabled under Categories to support on the Geocoding options page of the Locator Properties dialog box for the locator.Note:
When geocoding a table of addresses or places with a z-aware locator, it is recommended that you perform this operation in a local scene as the z-aware geocode results will be automatically loaded into the local scene with the elevation properties set to At an absolute height .
.
If the local scene contains the elevation surface that was used to
digitize the point reference data used to build the locator, set
the elevation of the geocode results to At an absolute height  on
the Layer Properties dialog box on the Elevation tab after
geocoding the table. If the elevation surface used to create the
reference data is not in the local scene, set the elevation of the geocode
results to Relative to the ground
on
the Layer Properties dialog box on the Elevation tab after
geocoding the table. If the elevation surface used to create the
reference data is not in the local scene, set the elevation of the geocode
results to Relative to the ground  after geocoding the table.
after geocoding the table.