Using a timeline, you can visualize data along a temporal axis. Timelines complement the spatial view of data on the map by showing where in time the data falls. By plotting the data along a timeline, you can understand its temporal order and discern temporal trends that emerge. When combined with time-enabling a map and using the time slider, a timeline gives a complete view of the temporal data and can enhance contextual understanding.
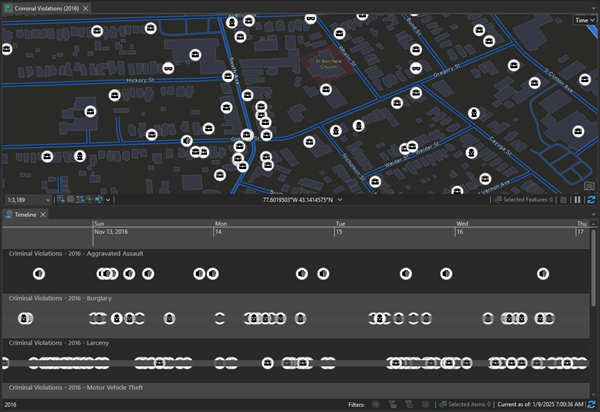
You can plot data on a timeline if time has been enabled on the layer on the Layer Properties dialog box. This data can have either a single time stamp in which case it appears as points along the timeline, or a start and an end time in which case it appears as a linear time span. Data that does not have a location assigned to it can also be plotted along a timeline. A timeline can contain multiple layers from the same map and unique values in a layer, allowing you to view multiple aspects of the data along the same temporal axis. These layers can be viewed in the same horizontal lane, or in distinct lanes, providing you a matrix you can use to compare features through both time and their category or lane.
Note:
Timelines only support Gregorian calendar dates.
Terminology
The following are terms are important to timeline management:
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
Timeline | A linear temporal axis containing a timescale and swimlanes. |
Timescale | Controls the extent of the timeline based on an increment of time. |
Timeslider | Controls the period of time that shows data on a map and timeline. |
Swimlane | A horizontal lane on the timeline defined by its layer and category. |
Time-enabled layer | A layer with temporal data that displays information based on the current time of the time slider. |
Timestamp | The time attached to a piece of data (feature, image, and so on). The time stamp can be a single instant or a time interval. |
Timespan | A symbol on the timeline with a leading marker, a trial, and ending marker. It represents data that takes place over a period of time. |
Summary View | Turns the timeline into a histogram wherein a user can specify the distribution of data into ranges known as bins. |
Binning Timespan | Used with Summary View, this controls the amount of binned features based on an increment of time. |
Learn more about temporal terminology.