You can use and work with Microsoft Excel files in ArcGIS AllSource in the same way as other tabular data sources. The only requirement to access and work with Excel files in ArcGIS AllSource is that the appropriate drivers must be downloaded and installed correctly on the computer on which ArcGIS AllSource is installed. For details, see Install the drivers to work with Microsoft Excel files.
Add Microsoft Excel files to a map
You add Microsoft Excel files to ArcGIS AllSource like other tabular data sources: click the Add Data button
 . When browsing to an Excel file, you must choose the table you want to open. For example, if you have an Excel workbook named Retail_Stores.xlsx that contains five worksheets—Stores, Sales.Revenue, @Customer Names, Customer#, and Top10Stores!—each worksheet is a separate table in ArcGIS AllSource.
. When browsing to an Excel file, you must choose the table you want to open. For example, if you have an Excel workbook named Retail_Stores.xlsx that contains five worksheets—Stores, Sales.Revenue, @Customer Names, Customer#, and Top10Stores!—each worksheet is a separate table in ArcGIS AllSource.
When accessed from ArcGIS AllSource, a worksheet is shown as a table with a dollar sign ($) at the end of its name. If the name of a worksheet contains one or more spaces, or starts with a non-letter character, the worksheet name and the dollar sign ($) will be enclosed in single quotes.
The following images show the difference in how a multi-sheet document is displayed in Microsoft Excel and displayed on the Add Data dialog box in ArcGIS AllSource:
-
Five worksheets are shown as they appear on the Sheet tab bar at the bottom of the Excel window.

- Available worksheets are shown in the Retail_Stores.xlsx workbook on the Add Data dialog box.

In this example, a worksheet named @Customer Names in Excel displays as '@Customer Names$' in ArcGIS AllSource. ArcGIS AllSource displays the worksheet's name in single quotes
because it contains a space.
ArcGIS AllSource attempts to maintain all characters in the worksheet or field name and displays this in the stand-alone table.
Note:
If the table name does not contain an expected character, it may have been replaced by the Microsoft driver before ArcGIS AllSource accessed it. This is known to occur for a small subset of characters, including but not limited to, .! becomes #_ as shown in the following image.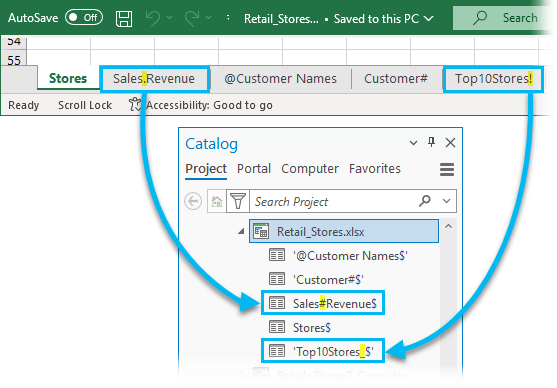
In the Catalog pane, you can access the Table Properties dialog box to review the properties for this stand-alone table.
You can also open the table in the Contents pane. However, you cannot edit the table or export records to an Excel format.
When used in a geoprocessing tool, the underlying table is used directly, so you may notice a slight change in the name.
For example, in ArcGIS AllSource, if you drag the Stores$ Excel worksheet into the Export Table geoprocessing tool or select it from the drop-down menu as the Input Table parameter, it will be represented in the Output Table parameter as Stores_ExportTable.

In another example, in ArcGIS AllSource, if you drag the 'Customer#$' Excel worksheet into the Export Table geoprocessing tool or select it from the drop-down menu as the Input Table parameter, it will be represented in the Output Table parameter as T_Customer__ExportTable.
Since 'Customer#$' is enclosed by single quotes, the Output Table parameter is prefixed with the letter T plus the single quotes, and the ($) are replaced with an underscore _. 
Note:
See Rename a worksheet to learn about Microsoft Excel worksheet names and limitations.
Format a table in Microsoft Excel for use in ArcGIS AllSource
You can work with Microsoft Excel files in ArcGIS AllSource in the same way as other tabular data sources, but there are a few limitations.
Follow these general best practices when creating Excel data to be used in ArcGIS AllSource:
- Ensure that the first row of the worksheet is properly formatted, since it will be used for the field names in ArcGIS.
Follow these best practices for field naming, particularly if you want to join an Excel table to another table:
- Field names must start with a letter.
- Field names must contain only letters, numbers, and underscores.
- Field names must not exceed 64 characters.
- If you have cells with numeric data, dates, and so on, ensure that the content is consistently formatted—in other words, ensure that all numeric data is actually numeric. If there are other types of data in those rows, the field is converted to text when the table is opened in ArcGIS AllSource.
Add a Microsoft Excel table to the map
You add Excel files to a project in the same way as other data: click the Add Data button on the Data tab, or use the Catalog pane.
- Click the Add Data button
 on the Data tab on the ribbon.
on the Data tab on the ribbon. The Add Data browse dialog box appears.
- Browse to the Excel workbook file and double-click the file.
- Click the table you want to add to the map.
- Click OK.
 .
.Refresh a Microsoft Excel table
You can refresh the Microsoft Excel workbook files that you use in ArcGIS AllSource to reflect updated data and schema edits made to any of the worksheets in the workbook.
Excel tables are read-only in ArcGIS AllSource; however, Excel files can be edited outside of ArcGIS AllSource while you have a worksheet open in the Catalog pane (stand-alone table layer).
When you refresh the workbook, ArcGIS AllSource reloads the Excel workbook file from disk, displays the updated (saved) data and schema changes made outside of ArcGIS AllSource, and refreshes any XY event layer created from the Excel file.
Use one of the following options to refresh an Excel workbook file in ArcGIS AllSource:
Note:
If you have the Microsoft Access Database Engine 2016 Redistributable driver installed on
your computer, then you will need to ensure that Microsoft Excel is closed before running the Refresh Excel geoprocessing tool or using the Refresh button  on the context menu of the Catalog pane.
on the context menu of the Catalog pane.
- Refresh
 —When an Excel workbook file is accessed from ArcGIS AllSource through the Catalog pane, Catalog view, or Script
tool,
right-click the Excel workbook file and click
Refresh
—When an Excel workbook file is accessed from ArcGIS AllSource through the Catalog pane, Catalog view, or Script
tool,
right-click the Excel workbook file and click
Refresh  on the context menu.
on the context menu.
- Refresh Excel tool—Use the Refresh Excel geoprocessing tool to refresh the workbook that you specify for the Input Excel File parameter.

- Select one or multiple files and click Menu
 at the top of the Catalog pane, and click Refresh
at the top of the Catalog pane, and click Refresh  .
. - At the top of the Catalog view, your current location is shown in the location bar. Browse to the item connection or the specific item you want to refresh. Next to the location bar, click Refresh
 .
. - When using the Browse button
 to populate a geoprocessing tool's input, next to the location bar, click Refresh
to populate a geoprocessing tool's input, next to the location bar, click Refresh  to get the latest information for the file used to populate the tool's input before running the tool.
to get the latest information for the file used to populate the tool's input before running the tool. 
Learn more about refreshing a location's content
Tip:
When refreshing Microsoft Excel files in ArcGIS AllSource, keep the following in mind:
Depending on the size of the Excel file, using the Refresh button
 can slow performance while ArcGIS AllSource reloads the file from disk and reloads the cache.
can slow performance while ArcGIS AllSource reloads the file from disk and reloads the cache. - A table error message may be returned if the schema of an Excel workbook file has been altered, such as renaming or deleting the worksheet, outside of ArcGIS AllSource to a point at which ArcGIS AllSource can no longer find references to the existing worksheets in the Excel file. If you receive an error message, remove the existing layer and add the Excel worksheet again.
Limitations
When working with Microsoft Excel files, keep the following in mind:
- ArcGIS supports both Excel 2003 and earlier .xls files and Excel 2007 .xlsx files. One advantage of Excel 2007 is that it allows much larger worksheets (1,048,576 rows by 16,384 columns) than you can have in Excel 2003 (65,536 rows by 256 columns).
- Field names are derived from the first row in each column of the worksheet. You can view the properties, set aliases for the field names, set field visibility, and set numeric formatting for the layer in the fields view.
- Excel does not enforce field types for values during data entry the way standard databases do, so the field type specified in Excel is not used in determining the field type exposed in ArcGIS. Instead, the field type in ArcGIS is determined by the Microsoft driver. If the driver finds mixed data types in a single field, that field will be returned as a string field, and the values will be converted to strings. If the Excel table will be exported, the size of text fields should be considered.
- You can directly export to Excel using the Table To Excel tool. You can also export tabular data to dBASE format, which can be opened in Excel 97–2003 and saved as an .xls file. Microsoft discontinued support for .dbf files in Office 2007.
- Excel files with password protection are not supported.