| Label | Explanation | Data Type |
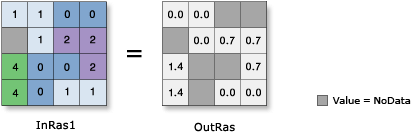
Input raster or constant value | Input values for which to find the natural logarithm (Ln). To use a number as an input for this parameter, the cell size and extent must first be set in the environment. | Raster Layer; Constant |
Return Value
| Label | Explanation | Data Type | Output raster | The output raster. The cell values are the base e (natural) logarithm of the input values. | Raster |