| Label | Explanation | Data Type |
Input conditional raster | The input raster representing the true or false result of the desired condition. It can be of integer or floating point type. | Raster Layer |
Input false raster or constant value | The input whose values will be used as the output cell values if the condition is false. It can be an integer or a floating-point raster, or a constant value. | Raster Layer; Constant |
Expression (Optional) | A logical expression that determines which of the input cells are to be true or false. The Where clause follows the general form of an SQL expression. It can be entered directly, for example, VALUE > 100, if you click the Edit SQL mode button | SQL Expression |
Return Value
| Label | Explanation | Data Type | Output raster | The output raster. If the conditional evaluation is true, NoData is returned. If false, the value of the second input raster is returned. | Raster |
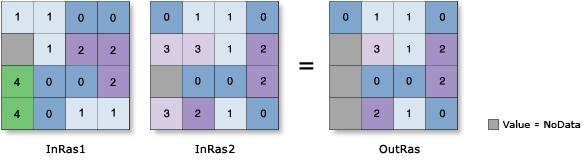
 . If in the
. If in the  , you can begin constructing the expression by clicking on the
, you can begin constructing the expression by clicking on the