| Label | Explanation | Data Type |
Input Table
| The input table. It can be a text file, CSV file, Excel file, dBASE table, or geodatabase table. | Table View |
Output Feature Class
| The output feature class containing geodetic or planar lines. | Feature Class |
X Field
| A numerical field in the input table containing the x-coordinates (or longitudes) of the starting points of lines to be positioned in the output coordinate system specified by the Spatial Reference parameter. | Field |
Y Field
| A numerical field in the input table containing the y-coordinates (or latitudes) of the starting points of lines to be positioned in the output coordinate system specified by the Spatial Reference parameter. | Field |
Distance Field | A numerical field in the input table containing the distances from the starting points for creating the output lines. | Field |
Distance Units
(Optional) | Specifies the units that will be used for the Distance Field parameter.
| String |
Bearing Field
| A numerical field in the input table containing bearing angle values for the output line rotation. The angles are measured clockwise from north. | Field |
Bearing Units
(Optional) | Specifies the units of the Bearing Field parameter values.
| String |
Line Type
(Optional) | Specifies the type of line that will be constructed.
| String |
ID
(Optional) | A field in the input table. This field and the values are included in the output and can be used to join the output features with the records in the input table. | Field |
Spatial Reference
(Optional) | The spatial reference of the output feature class. The default is GCS_WGS_1984 or the input coordinate system if it is not Unknown. | Spatial Reference |
Preserve attributes (Optional) | Specifies whether the remaining input fields will be added to the output feature class.
| Boolean |
Summary
Creates a feature class containing geodetic or planar line features from the values in an x-coordinate field, y-coordinate field, bearing field, and distance field of a table.
Illustration
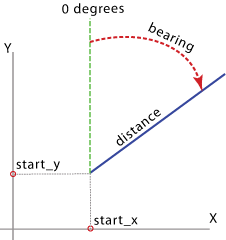
Usage
Output lines are constructed from field values. The field values include the following:
- The x- and y-coordinates of a starting point
- The distance from the starting point
- The bearing angle
When the output lines are geodetic, the x- and y- coordinates and distance are measured on the surface of the earth, and the bearing angle is measured from north. When the output lines are planar, the x- and y- coordinates and distance are measured on the projected plane, and the bearing angle is measured clockwise from grid north (vertical up on the map).
A geodetic line is a curve on the surface of the earth. However, a geodetic line feature is not stored as a parametric (true) curve in the output; rather, it is stored as a densified polyline representing the path of the geodetic line. If the length of a geodetic line is relatively short, it may be represented by a straight line in the output. As the length of the line increases, more vertices are used to represent the path.
When the output is a feature class in a geodatabase, the values in the Shape_Length field are always in the units of the output coordinate system specified by the Spatial Reference parameter, and they are the planar lengths of the polylines. To measure a geodesic length or distance, use the ArcGIS Pro Measure tool and choose the Geodesic, Loxodrome, or Great Elliptic option accordingly before taking a measurement.
Parameters
arcpy.management.BearingDistanceToLine(in_table, out_featureclass, x_field, y_field, distance_field, {distance_units}, bearing_field, {bearing_units}, {line_type}, {id_field}, {spatial_reference}, {attributes})| Name | Explanation | Data Type |
in_table | The input table. It can be a text file, CSV file, Excel file, dBASE table, or geodatabase table. | Table View |
out_featureclass | The output feature class containing geodetic or planar lines. | Feature Class |
x_field | A numerical field in the input table containing the x-coordinates (or longitudes) of the starting points of lines to be positioned in the output coordinate system specified by the spatial_reference parameter. | Field |
y_field | A numerical field in the input table containing the y-coordinates (or latitudes) of the starting points of lines to be positioned in the output coordinate system specified by the spatial_reference parameter. | Field |
distance_field | A numerical field in the input table containing the distances from the starting points for creating the output lines. | Field |
distance_units (Optional) | Specifies the units that will be used for the distance_field parameter.
| String |
bearing_field | A numerical field in the input table containing bearing angle values for the output line rotation. The angles are measured clockwise from north. | Field |
bearing_units (Optional) | Specifies the units of the bearing_field parameter values.
| String |
line_type (Optional) | Specifies the type of line that will be constructed.
| String |
id_field (Optional) | A field in the input table. This field and the values are included in the output and can be used to join the output features with the records in the input table. | Field |
spatial_reference (Optional) | The spatial reference of the output feature class. A spatial reference can be specified as any of the following:
| Spatial Reference |
attributes (Optional) | Specifies whether the remaining input fields will be added to the output feature class.
| Boolean |
Code sample
Convert bearing and distance information into a line.
# Import system modules
import arcpy
# Local variables
input_table = r'c:\workspace\LOBtraffic.dbf'
output_fc = r'c:\workspace\SOPA.gdb\lob_traf001'
# BearingDistanceToLine
arcpy.BearingDistanceToLine_management(input_table, output_fc, 'X', 'Y',
'NAUTICAL_MILES', 'azim', 'DEGREES',
'GEODESIC', 'recnum')