A subset of cells can be extracted to a new raster in several ways—by selecting an attribute or a defined shape or by using another raster.
Extraction by attribute
Cells that meet a specified attribute query can be extracted to a new output raster using the Extract by Attributes tool.
Examples of applications for this tool include the extraction of all cells that have a slope greater than 10 percent or the extraction of all cells attributed with zoning for commercial development. All cells that meet the query will return, for the cell location, the original value that was queried.
The cells that meet the specified query need not be contiguous.
Extraction by shape
You can extract cells based on a specified shape. You can extract only the cells that fall inside the shape or those that fall outside the shape. You can extract by a circle, rectangle, or polygon.
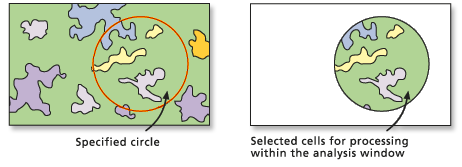
Circular area extraction
To perform a circular extraction, use the Extract by Circle tool.
The location of the center of the circle and the radius must be specified.
In the image below, all cells (cell centers) that fall within the circle are extracted.
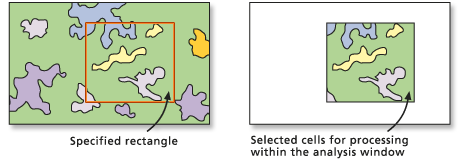
Rectangular area extraction
To perform a rectangular extraction, use the Extract by Rectangle tool.
The lower left and upper right corners of the rectangle must be identified.
In the image below, the cells inside the specified rectangular shape are extracted.
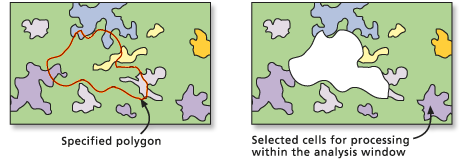
Polygonal area extraction
To perform an extraction based on a polygonal shape, use the Extract by Polygon tool.
The location of the vertices of the polygon must be specified.
In the image below, an extraction polygon was identified, but a parameter was specified to extract the cells outside rather than inside the polygon.
Extraction by location
Cells can be extracted based on their spatial location. The cells to extract can be determined by individual point locations or from a group of locations of any size or shape as identified by a mask.
Point location extraction
You can extract particular cells from a raster by defining a list of the coordinate points of interest.
To perform an extraction based on point location use the Extract by Points tool.
The points must be identified by their x,y coordinate locations.
Extraction by mask
You can use a mask to identify cells that will be extracted to a new raster. The mask can be either a raster or a feature dataset.
To perform this type of extraction, use the Extract by Mask tool.
There are a number of ways to create a mask raster using various ArcGIS Spatial Analyst tools.
You can control whether cells inside or outside the locations defined by the input mask are selected and written to the output raster.
Using the Extract by Mask tool, as shown in the image below, the locations that are not NoData in a mask raster retain the value assigned to those locations in the Input raster parameter value.
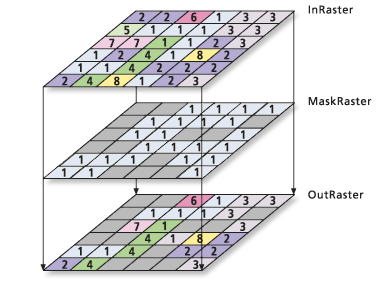
If a feature dataset is used for the mask, only cells that fall within the specified shape of the feature data are included when performing the analysis.