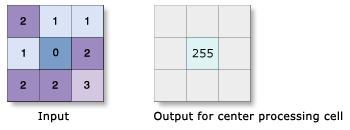
The Focal Flow tool uses the immediate 3 x 3 neighborhood around each cell to determine which of its eight neighbors flows into it. Flow is defined by any cell within the neighborhood that has a higher value than the processing cell. Many times the values represent fluid movement, such as water moving across an elevation or slope surface, but flow can be any movement you define, such as the way contaminants move to a location of lower concentration. Focal Flow uses a "moving window" approach to process through a dataset, in a similar manner to how the Focal Statistics tool works. However, the way in which the output values are calculated is not the same.
To test whether a particular neighborhood cell will flow into the processing cell, the value of each neighborhood cell is subtracted from the processing cell. If a value is positive, the neighborhood cell does not flow into the processing cell; if it is negative, it does. If no cells flow into the processing cell, the location will receive a value of 0. If a threshold value has been entered, the difference between the value of the neighborhood cell minus the value of the processing cell must be greater than the threshold for flow to occur. If it is not, there is no flow from the neighborhood cell.
The management of the combination of flow from multiple neighborhood cells into a single processing cell is accomplished through the binary representation of the processing cell. Each bit of the binary representation for the processing cell correlates to a neighborhood cell location. The cell to the immediate right of the processing cell is given the value 1, the neighbor to the lower right is 2, the neighbor directly below is 4, and so forth—until the value of 128 (powers of two, since representation occurs in binary) is reached for the last neighbor to the upper right.
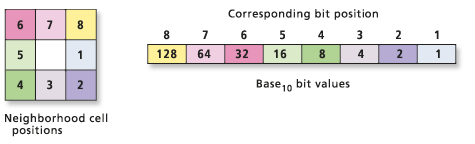
If a neighborhood cell flows into the processing cell, the bit that represents the neighborhood location (see preceding diagram) is turned on, or assigned a 1. If a neighborhood cell does not flow into the processing cell, the bit that represents the location is turned off, or assigned value 0. Once all neighborhood locations have been tested for flow, none, one, several, or all bits can be turned on (assigned a 1). The binary representation for all bits is converted back to base10 in accordance with the flow-bit pattern. The base10 number is then assigned to the processing cell. The encoding assigns a unique number to each possible combination of upstream numbers. The total number of combinations of flow into a processing cell is 255.
Examples
Some examples demonstrating how the output value is derived follow:
- Cell that receives flow from the upper left adjacent cell
Flow from the upper left adjacent cell has a neighborhood bit position of 6 (see the previous Focal Flow direction encoding graphic). The base10 value that corresponds to this bit position is 32.
- Cell receiving flow from several cells
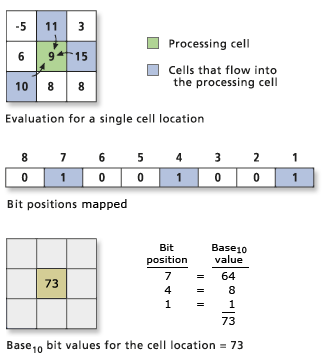
In the following graphic, the processing cell has three surrounding cells that have a higher value. These are the cell that is immediately to the right (the first bit position), the cell to the lower left (the fourth bit position), and the cell just above it (the seventh bit position). Consequently, the first, fourth, and seventh bits are turned on, or set to 1. This bit pattern evaluates to 73 in base10 and is written to the location of the processing cell on the output raster.
- Cell receiving flow from all eight surrounding cells
Consider a cell into which all adjacent neighbors would flow. The output value would receive a value of the sum of all bit position values from 1 through 128. The resulting value, calculated by 128 + 64 + 32 + 16 + 8 + 4 + 2 + 1, would equal 255.