Available with Image Analyst license.
Change detection using multiband imagery is based on computing the spectral difference on a pixel-by-pixel basis.
Comparing multiband image data allows you to identify areas that have experienced a change in spectral response, usually over a period of time. ArcGIS AllSource provides a few methods for comparing multiband images.
The spectral change methods are available when a mutliband raster is selected in the Contents pane.
The Compute Change raster function computes the difference between two raster layers on the fly. Only the pixels within the visible extent are processed, and if zoomed out beyond the source resolution of the input data, the pixels are resampled to a larger size to speed up processing. This is a way to compute change for quick visualization and assessment of change. You can combine this function with other raster functions for a more complex workflow.
The Compute Change Raster geoprocessing tool computes the difference between two raster datasets and generates a new raster dataset containing the change information. You can combine this tool with other tools for a more complex workflow.
The Change Detection Wizard combines tools and functions to guide you through the process of performing categorical change detection, pixel value change detection, spectral change detection, or time series change detection. You can compare two raster datasets, or two slices in a multidimensional raster dataset.
Change Detection Wizard
The Change Detection Wizard is launched from the Change Detection drop-down button on the Imagery tab, in the Analysis group. The button is unavailable if you are not working in a 2D map scene, or if you do not have the Image Analyst extension.
Configure pane
The first pane in the Change Detection Wizard is the Configure pane, where you set the Change Detection Method value. To compare multiband datasets, set Change Detection Method to Spectral Change.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
From Raster | The first raster to be used in the computation. To evaluate change from time 1 (earlier) to time 2 (later), enter the time 1 raster. |
To Raster | The second raster to be used in the computation. To evaluate change from time 1 (earlier) to time 2 (later), enter the time 2 raster. |
To compare two slices in a multidimensional dataset, enter the multidimensional raster as the From Raster parameter. The Configure pane updates with the parameters in the table below.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
Variable | The variable to be analyzed. |
Dimension | The dimension field to use to compare slices. |
From Slice | The first slice to be used in the computation. To evaluate change from time 1 (earlier) to time 2 (later), enter the time 1 slice. |
To Slice | The second slice to be used in the computation. To evaluate change from time 1 (earlier) to time 2 (later), enter the time 2 slice. |
Processing Extent | The processing extent for the output. |
X Skip Factor | The x skip factor used to calculate statistics and the histogram for the change raster. |
Y Skip Factor | The y skip factor used to calculate statistics and the histogram for the change raster. |
Spectral Difference pane
The Spectral Difference pane allows you to specify how to compare the input multiband imagery and specify the type of change information to calculate.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
Difference Type | The difference method to use in the calculation.
|
Cell Size Type |
|
Extent Type |
|
Click Preview to add a preview layer to the map, using the options you specified. You can modify the options and click Update Preview to refresh the preview layer with the new options.
Note:
The preview layers are generated using raster functions. When zoomed out beyond the source resolution, raster functions process the data using a resampled pixel size. To ensure the preview looks the way you want to see in your final result, zoom to the source resolution of the data. Right-click the preview layer and click Zoom to Source Resolution.
Classify Difference pane
The Classify Difference pane allows you to explore the differences in pixel spectra on the fly in the map, and use the information to classify the results.
The Explore Differences section is in the upper half of the Classify Difference pane. 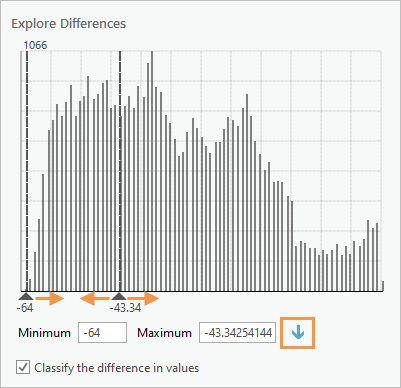
To skip classification and retain the original pixel value differences, uncheck the Classify the difference in values parameter, and click Next to move to the next pane.
Use the interactive histogram to generate classes
To use the interactive histogram to generate classes, complete the following steps:
- Drag the minimum and maximum handles in the histogram until you have identified the change information that is important to your analysis (for example, strong negative change).
- Click the Add New Class button
 .
. The minimum and maximum values selected in the histogram are added as minimum and maximum class values in the Classify Output table at the bottom of the pane.
- In the Classify Output table, add the class value (an integer) to the Output field and the name of the class to the Class Name field.
These are required.
- Specify the color to use to symbolize the class.
Manually generate classes
To manually add class information without using the interactive histogram, complete the following steps:
- Click the Generate button
 .
. - In the Generate pane, set the Maximum Value parameter to the number of classes you want to generate.
You can specify a base name for the classes associated with each unique value. You can also specify the color scheme and the transparency for the class symbology.
- Click OK.
- In the Classify Output table, type the Minimum and Maximum difference field values for each class.
Click Preview to add a preview layer to the map, using the options you specified. You can modify the options and click Update Preview to refresh the preview layer with the new options.
Note:
The preview layers are generated using raster functions. When zoomed out beyond the source resolution, raster functions process the data using a resampled pixel size. To ensure the preview looks the way you want to see in your final result, zoom to the source resolution of the data. Right-click the preview layer and click Zoom to Source Resolution.
Post-processing pane
The Post-processing pane allows you to smooth your results and generate an output.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
Smoothing Neighborhood | The size of the focal neighborhood to use, in pixel rows and columns, to smooth your results.
|
Statistics Fill Method |
The statistical method to use to recalculate pixel values for a smoother result. |
Save Result As | Specify the output type to generate.
|
Output Dataset | The name of the output dataset. This parameter is only available if Save Result As is set to Raster Dataset or Feature Class. If the output is a raster dataset, specify the file extension to generate a raster in a supported format. |
For additional smoothing options, you can use the Statistics raster function on your results. Choose None as the Smoothing Neighborhood in the wizard, and use the Statistics raster function on the output raster dataset.
Click Preview to add a preview layer to the map, using the options you specified. You can modify the options and click Update Preview to refresh the preview layer with the new options.
Note:
The preview layers are generated using raster functions. When zoomed out beyond the source resolution, raster functions process the data using a resampled pixel size. To ensure the preview looks the way you want to see in your final result, zoom to the source resolution of the data. Right-click the preview layer and click Zoom to Source Resolution.
Compute a spectral angle difference
The following example computes the spectral angle difference between two Landsat 8 images.
- Add the two Landsat 8 images to the map.
- With the earlier image layer selected in the Contents pane, launch the Change Detection Wizard from the Imagery tab in the Analysis group.
In the Configure pane, set the Change Detection Method to Spectral Change.
- Set the From Raster parameter to the earlier raster layer.
- Set the To Raster parameter to the later raster layer.
- Click Next.
- In the Band Difference pane, set Difference Type to Spectral Angle Difference.
- Set the Cell Size Type parameter to Max of and the Extent Type parameter to Intersection of.
- Click Next.
- In the Classify Difference pane, drag the minimum histogram handle until the results in the preview mask are constrained to your area of interest. Leave the maximum histogram handle at the largest positive value. Click Add New Class.
This reduces the presence of background or small-angle, ambient change in the results.
- In the Classify Output table, set the Output field value to 1, type an appropriate name for the Class Name field, and use the color picker to select a red color.
- Click Next.
- In the Post-processing pane, set the Smoothing Neighborhood parameter to 3 x 3 and the Statistics Fill Method parameter to Majority.
- For the Output Dataset parameter, type Spectral_angle_change.tif and click Run.
- When the dataset is added to the map, click Finish to close the Change Detection Wizard.