Use the Terrain service
Once you've published the terrain image service, you can use it in ArcGIS 10.9.1 or later, ArcGIS Pro 2.9 or later, and ArcGIS Online. Terrain is a dynamic image service comprising multiple sources and resolutions ranging from 1,000 meters to 0.25 meters. It can be used for visualization and analysis.
Use the service in ArcGIS Desktop
Use the service in ArcGIS Pro
To use the Terrain service in ArcGIS Pro, complete the following steps:
- Start ArcGIS Pro and choose the Map project template.
- On the Insert tab, click Connections and choose New ArcGIS Server.
- Provide the URL of the server where you published the Terrain service.
- On the Map tab, click Add Data > Data.
- Click Servers, double-click the server connection, and select the Terrain service.
The Terrain service is added to the map. By default, the service renders as an elevation (DEM) raster.
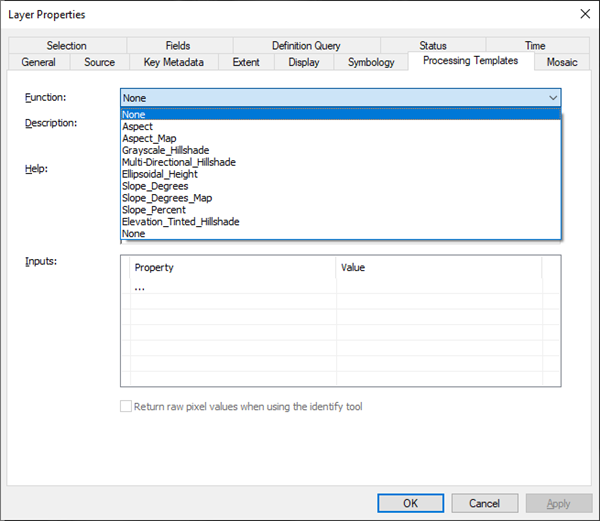
- Right-click Terrain, and click Properties > Processing Templates.
- From the Processing Template drop-down list, choose one of the functions defined on the service.
- Click OK.
The map dynamically renders the elevation derivative selected from the drop-down list.
Use the service in ArcMap
To use the Terrain service in ArcMap, complete the following steps:
- In the Catalog window, make an ArcGIS server connection to the server that is hosting the elevation services.
- Start ArcMap and add or drag the
Terrain service to the map.
By default, the service renders as an elevation (DEM) raster.
- Right-click Terrain and click Properties > Processing Templates.
- From the Function drop-down list, choose one of the functions defined on the service.
- Click OK.
The raster function dynamically renders the elevation derivative selected from the drop-down list.
Use Terrain for analysis
The Terrain service includes data with resolutions ranging from more than 1,000 meters to approximately 0.25 meters in some limited areas, and each record (raster item) is populated with the Dataset_ID and ProductName tags, which can be used for filtering. Since the service is composed of multiple-resolution datasets, the records must be filtered based on a single resolution (or dataset) before consuming it for analysis. Use the Make Image Server Layer geoprocessing tool to create a temporary layer that can be used in other geoprocessing tools. In the following scenario, analysis is done in the Redlands, California, area:
- Add the Terrain service to ArcMap.
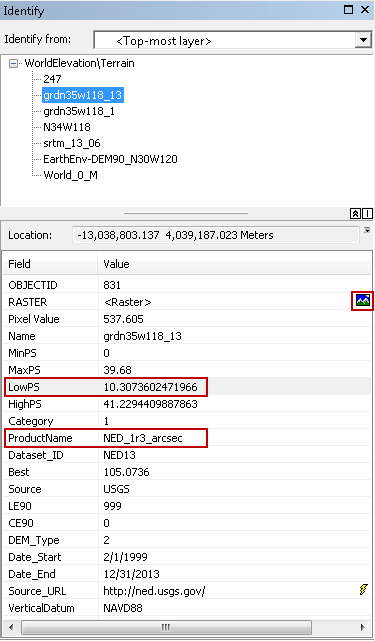
- Zoom to the Redlands area of interest (AOI) and click Identify on the Terrain
service.
A list of raster items is returned.
- Examine the LowPS (cell resolution in meters) values of rasters in the Identify result window.
- Determine the resolution you need to work with.
Note the ProductName field value. This example is for the NED_1r3_arcsec dataset, which has a resolution of approximately 10.3 meters.
- Open the Make Image Server Layer tool.
- Define the parameters.
- Specify the input image service.
- Set Expression to "ProductName" = 'NED_1r3_arcsec'.
- Optionally, set the output coordinates from the env setting, if the request being made is different from the image service coordinates (Web Mercator).
- Specify the extent.
- Specify the Output Cell Size value as 10.3.
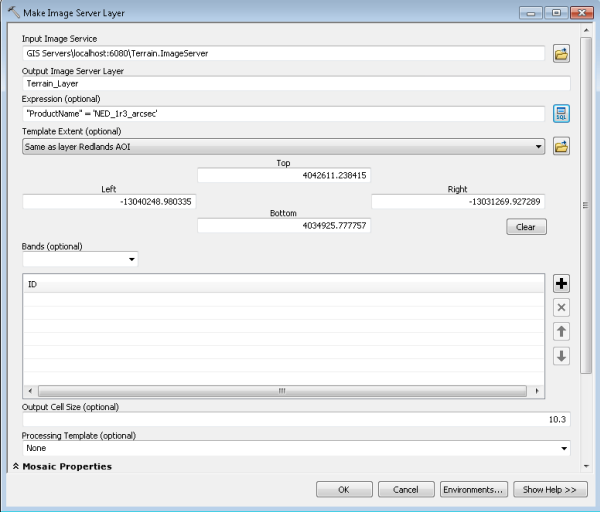
- Click OK to run the tool.
A temporary layer is generated with cell size, coordinate system, extent, and expression parameters defined in the tool. This temporary elevation layer can now be used in other geoprocessing tools for further analysis.
The request size of the output layer is limited to 5,000 by 5,000 pixels (property defined on mosaic datasets).
For information about the Make Image Server Layer tool, see Make Image Server Layer in the ArcMap help under Tools > Tool reference > Data Management toolbox > Layers and Table Views toolset.
For information about using mosaic datasets and image services in geoprocessing tools, see Using mosaic datasets and image services in analysis and geoprocessing in the ArcMap help under Manage Data > Data types > Raster and images > Processing and analyzing raster data.
Use the service in ArcGIS Online or Portal for ArcGIS
To use the Terrain service in ArcGIS Online or Portal for ArcGIS, complete the following steps:
- Go to the REST endpoint of the Terrain service, for example, https://localhost:6443/arcgis/rest/services/Terrain/ImageServer.
- Click ArcGIS Online Map Viewer.
The Terrain service opens in Map Viewer in a browser. By default, it renders as elevation (DTM).
- Click Terrain > More Options > Image Display > Renderer to choose from the
server functions defined on the service.
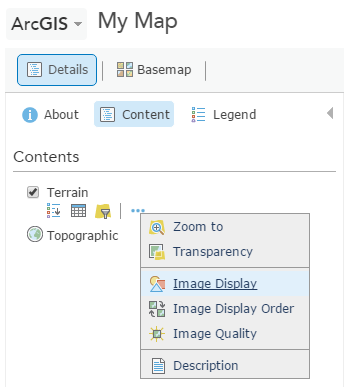
- Choose Grayscale_Hillshade Renderer (that is, server
raster function) from the drop-down list and click Apply.
The map renders the hillshade.
Data coverage map
You can explore the DataExtentsMap.mxd file at \\<server-ip>\CollectionX_source_documents\data\WorldElevation\DataExtentsMap, where CollectionX is the collection where the Terrain image service is located: Collection1 (World Basic), Collection2 (World Standard), Collection3 (World Advanced), Collection4 (North America Standard), or Collection5 (North America Advanced). This map provides the coverage extent of various datasets composing the Terrain service. The map document (.mxd) can be published as a map service.
For information about publishing a map document (.mxd) as a map service, see Publish a map service from ArcMap in the ArcMap help under Publish services > Publish map services > Publishing your map as a service.
Use the Terrain3D service
The sections below describe how to use the Terrain3D service.
Use the service in ArcGIS Pro
To use the Terrain3D service in ArcGIS Pro, complete the following steps:
- Start ArcGIS Pro and choose the Global_Scene project template.
- On the Insert tab, click Connections and choose New ArcGIS Server.
- Provide the server URL where you published the Terrain3D service.
- On the Map tab, click Add Data > Elevation Source.
- Click
Servers, double-click the server connection, and
select the
Terrain3D service.
The elevation source is added to the ground.
- Optionally, turn off or remove the default ArcGIS Online elevation layer (WorldElevation3D/Terrain3D) from Ground.
- Zoom to any location and tilt the scene to view the oblique views.
With ArcGIS Pro, you can add your unique 2D and 3D data layers to the scene. Your data is added to the elevation surface. If your data has defined elevation (z-coordinates), this information is honored in the scene. You can then share your work as a web scene with others in your organization or with the public.
For information about scenes in ArcGIS Pro, see Scenes in the ArcGIS Pro help under Maps and scenes > Author maps and scenes.
Use the service in ArcGIS Online or Portal for ArcGIS
To use the Terrain3D service in ArcGIS Online or Portal for ArcGIS, complete the following steps:
- Sign in to ArcGIS Online or your organization's Portal for ArcGIS.
- Open Scene Viewer.
- On the Designer toolbar, click Add Layers
 to add layers, and then click ArcGIS web service
to add layers, and then click ArcGIS web service  to open the Enter Layer URL pane.
to open the Enter Layer URL pane. - In the Enter Layer URL pane, in the Layer URL text box, enter the REST endpoint of the Terrain3D service published on your server, for example, https://localhost:6443/arcgis/rest/services/Terrain3D/ImageServer.
- Click
Add to add the layer to your scene.
The Terrain3D elevation layer is added as Ground.
Using Scene Viewer in ArcGIS Online, you can create and interact with 3D scenes. Your data is added to the elevation surface. If your data has defined elevation (z-coordinates), this information is honored in the scene. You can then share your work as a web scene with others in your organization or with the public.
For information about using the 3D scene viewer, see Get started with Scene Viewer in the ArcGIS Online help.